Category:Scraping Use Cases
Scraping Amazon Search Results, Product Ads, Related Searches

Software Engineer
Almost every ecom product research project, competitor analysis, and price monitoring starts at the same place: Amazon search.
Organic results give you top products. Related searches give you the keywords. Sponsored placements give you the ad strategies your competitors are running.
In this guide, we'll extract all three using Python.
[All code available on GitHub] ⚙
Prerequisites
No heavy tech stack here. Just a few simple things to get started:
Pick a Target URL
I've been meaning to buy a laptop stand for a while now, so this article is the perfect excuse to finally do some research.
We'll use laptop stands as our search query throughout this guide.

Install Required Libraries
We'll use requests to send HTTP requests and beautifulsoup4 to parse the HTML:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4Generate Scrape.do Token
Amazon uses AWS WAF to block bots. Every request is analyzed for IP reputation, headers, and browsing patterns.
We'll use Scrape.do to handle this, but the code in this guide works with any scraping API or your own bypass solution.
Scrape.do's Amazon Scraper API gives us:
- Automatic proxy rotation and WAF bypass
- Geo-targeting with specific ZIP codes (this affects prices and availability)
- Raw HTML output for custom parsing
To get your token, sign up here and grab it from the dashboard:

Scrape Amazon Search Results
From the search results, we'll first scrape product information and navigate through multiple pages of search results, parsing individual product data and handling pagination.
We can either use the next-page button to iterate through results or request each page directly by adding the page number to the URL.
Using the next-page button might get blocked by Amazon since they monitor these navigation elements for bot traffic. Plus, it consumes more resources as it requires rendering the page.
To avoid blocks, we'll request each search page one-by-one using the URL structure, until we reach our maximum page count.
Send a Request to Amazon
Let's start with our imports and configuration:
import urllib.parse
import csv
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Configuration
token = "<SDO-token>"
search_query = "laptop stands"
geocode = "us"
zipcode = "10001"
max_result_page = 4
current_result_page = 1
all_products = []I set max_result_page to 4 for this example, but you can increase it based on how many pages you need.
Now we'll build the request. We're using the Amazon Scraper API's raw HTML endpoint with geo-targeting:
# Build search URL with page number
target_url = f"https://www.amazon.com/s?k={urllib.parse.quote_plus(search_query)}&page={current_result_page}"
targetUrl = urllib.parse.quote(target_url)
apiUrl = "https://api.scrape.do/plugin/amazon/?token={}&url={}&geocode={}&zipcode={}&output=html".format(token, targetUrl, geocode, zipcode)
response = requests.request("GET", apiUrl)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")The geocode and zipcode parameters ensure we get localized prices and availability for a specific region.
Parse Product Data
Each product element has s-result-item as its class. We'll extract the name, price, link, and image from each:
product_elements = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "s-result-item"})
for product in product_elements:
try:
name = product.select_one("h2 span").text
try:
price = str(product.select("span.a-price")).split('a-offscreen">')[1].split('</span>')[0]
except:
price = "Price not available"
link = product.select_one(".a-link-normal").get("href")
image = product.select_one("img").get("src")
if name:
all_products.append({"Name": name, "Price": price, "Link": link, "Image": image})
except:
continueThe price extraction looks a bit hacky, but Amazon's price structure is nested in multiple spans. We're grabbing the a-offscreen span which contains the clean price text.
Handle Pagination
To scrape multiple pages, we wrap everything in a loop and increment the page number:
while True:
# Build search URL with page number
target_url = f"https://www.amazon.com/s?k={urllib.parse.quote_plus(search_query)}&page={current_result_page}"
targetUrl = urllib.parse.quote(target_url)
apiUrl = "https://api.scrape.do/plugin/amazon/?token={}&url={}&geocode={}&zipcode={}&output=html".format(token, targetUrl, geocode, zipcode)
response = requests.request("GET", apiUrl)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
# Parse products on the current page
product_elements = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "s-result-item"})
if current_result_page > max_result_page:
break
for product in product_elements:
try:
name = product.select_one("h2 span").text
try:
price = str(product.select("span.a-price")).split('a-offscreen">')[1].split('</span>')[0]
except:
price = "Price not available"
link = product.select_one(".a-link-normal").get("href")
image = product.select_one("img").get("src")
if name:
all_products.append({"Name": name, "Price": price, "Link": link, "Image": image})
except:
continue
current_result_page += 1All product information is now stored in all_products. Let's export it.
Export to CSV
We'll use Python's built-in CSV library. Here's the full code with the export logic added:
import urllib.parse
import csv
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Configuration
token = "<SDO-token>"
search_query = "laptop stands"
geocode = "us"
zipcode = "10001"
max_result_page = 4
current_result_page = 1
all_products = []
# Loop through all result pages
while True:
# Build search URL with page number
target_url = f"https://www.amazon.com/s?k={urllib.parse.quote_plus(search_query)}&page={current_result_page}"
targetUrl = urllib.parse.quote(target_url)
apiUrl = "https://api.scrape.do/plugin/amazon/?token={}&url={}&geocode={}&zipcode={}&output=html".format(token, targetUrl, geocode, zipcode)
response = requests.request("GET", apiUrl)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
# Parse products on the current page
product_elements = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "s-result-item"})
if current_result_page > max_result_page:
break
for product in product_elements:
try:
name = product.select_one("h2 span").text
try:
price = str(product.select("span.a-price")).split('a-offscreen">')[1].split('</span>')[0]
except:
price = "Price not available"
link = product.select_one(".a-link-normal").get("href")
image = product.select_one("img").get("src")
if name:
all_products.append({"Name": name, "Price": price, "Link": link, "Image": image})
except:
continue
current_result_page += 1
# Export to CSV
csv_file = "amazon_search_results.csv"
headers = ["Name", "Price", "Link", "Image"]
with open(csv_file, "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as file:
writer = csv.DictWriter(file, fieldnames=headers)
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(all_products)
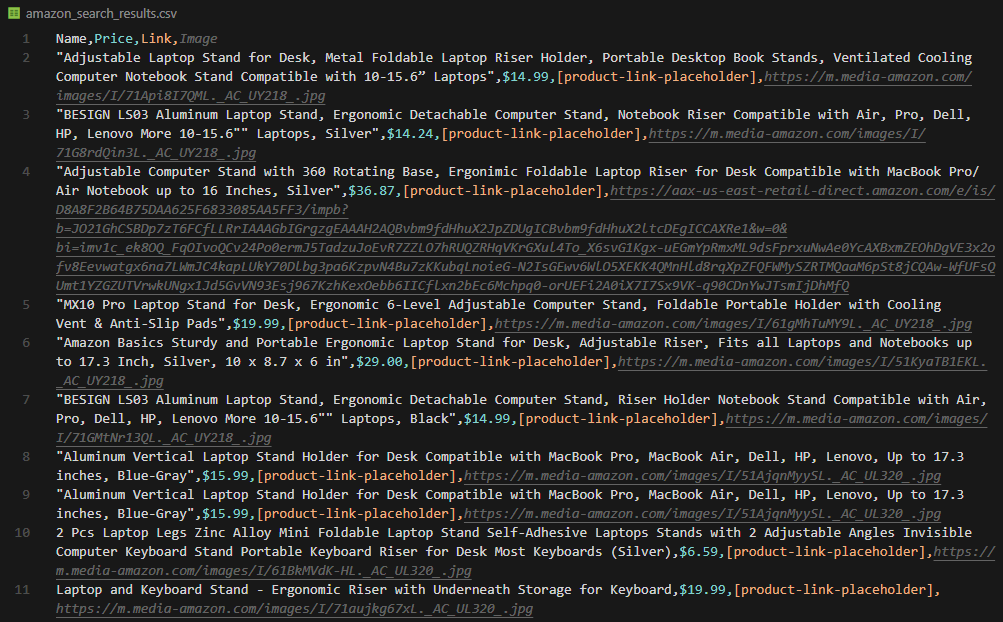
print(f"Data successfully exported to {csv_file}")Your amazon_search_results.csv should look like this:
Or You Pick the Easy Way
If you just need product listings without custom parsing, Scrape.do can return structured JSON directly.
The /search endpoint handles all the parsing for you:
import requests
token = "<SDO-token>"
keyword = "laptop stands"
geocode = "us"
zipcode = "10001"
apiUrl = f"https://api.scrape.do/plugin/amazon/search?token={token}&keyword={keyword}&geocode={geocode}&zipcode={zipcode}"
response = requests.get(apiUrl)
data = response.json()
print(data)The response includes everything pre-parsed:
{
"keyword": "laptop stands",
"page": 1,
"totalResults": "10,000+ results",
"products": [
{
"asin": "B0BLRJ4R8F",
"title": "Amazon Basics Laptop Stand...",
"url": "/dp/B0BLRJ4R8F",
"imageUrl": "https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/...",
"price": { "currencyCode": "USD", "amount": 28.57 },
"rating": { "value": 4.6, "count": 12453 },
"isSponsored": false,
"isPrime": true,
"position": 1
}
]
}Scrape Amazon Related Searches
Related searches appear at the bottom of Amazon search results. They're useful for keyword research, finding product variations, and understanding how customers search.
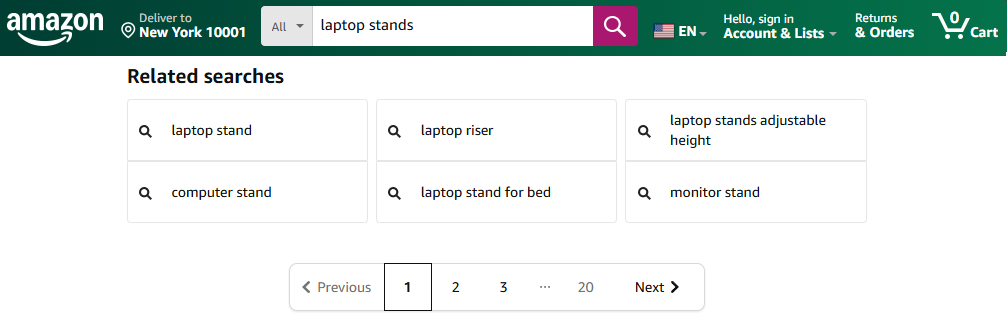
We'll use the same request setup, but this time we're parsing the related searches section instead of product listings.
Each related search term sits inside a div with classes a-box-inner and a-padding-mini.
import urllib.parse
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Configuration
token = "<SDO-token>"
search_query = "laptop stands"
geocode = "us"
zipcode = "10001"
# Build search URL (no pagination needed - related searches appear on page 1)
target_url = f"https://www.amazon.com/s?k={urllib.parse.quote_plus(search_query)}"
targetUrl = urllib.parse.quote(target_url)
apiUrl = "https://api.scrape.do/plugin/amazon/?token={}&url={}&geocode={}&zipcode={}&output=html".format(token, targetUrl, geocode, zipcode)
response = requests.request("GET", apiUrl)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
# Related searches are in a carousel at the bottom of search results
# Each term is wrapped in a div with classes "a-box-inner" and "a-padding-mini"
related_searches = []
for div in soup.find_all("div", class_="a-box-inner a-padding-mini"):
# Extract clean text, stripping whitespace
text = div.get_text(strip=True)
if text:
related_searches.append(text)
print("Related searches:")
for i, term in enumerate(related_searches, 1):
print(f" {i}. {term}")Here's your terminal output:
Related searches:
1. laptop stand for desk
2. laptop stand adjustable height
3. laptop stand for bed
4. laptop cooling stand
5. portable laptop stand
6. laptop stand with fan
7. laptop riser stand
8. laptop stand aluminumScrape Product Ads and Sponsored Brands from Amazon
Sponsored products on Amazon search results are a goldmine for anyone running PPC campaigns.
You can see exactly which products your competitors are pushing, what ad formats they're using, and where they're placing their budget.
But it's easier said than done, as the sponsored products in search results have multiple structures:
- Video ads at the top and scattered through results
- In-search ads that look like regular products but are marked "Sponsored"
- Carousels featuring multiple products from a single brand
- Featured brands in a dedicated section
But that doesn't stop us, we'll extract all of them :)
First, let's set up the request and data structure:
import urllib.parse
import json
import re
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Configuration
token = "<SDO-token>"
search_query = "gaming headsets"
geocode = "us"
zipcode = "10001"
# Build search URL
target_url = f"https://www.amazon.com/s?k={urllib.parse.quote_plus(search_query)}"
targetUrl = urllib.parse.quote(target_url)
apiUrl = "https://api.scrape.do/plugin/amazon/?token={}&url={}&geocode={}&zipcode={}&output=html".format(token, targetUrl, geocode, zipcode)
response = requests.request("GET", apiUrl)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
# Initialize output structure for all ad types
sponsored_data = {
"video_ads": [],
"in_search": [],
"carousels": [],
"featured_brands": []
}Now let's extract each ad type.
1. Extract Video Ads
Video ads come in two formats: top featured videos with product carousels, and single-product video ads scattered through results.
1.1. Top Video Ads
These appear at the top of search results with a brand logo, headline, and product carousel.
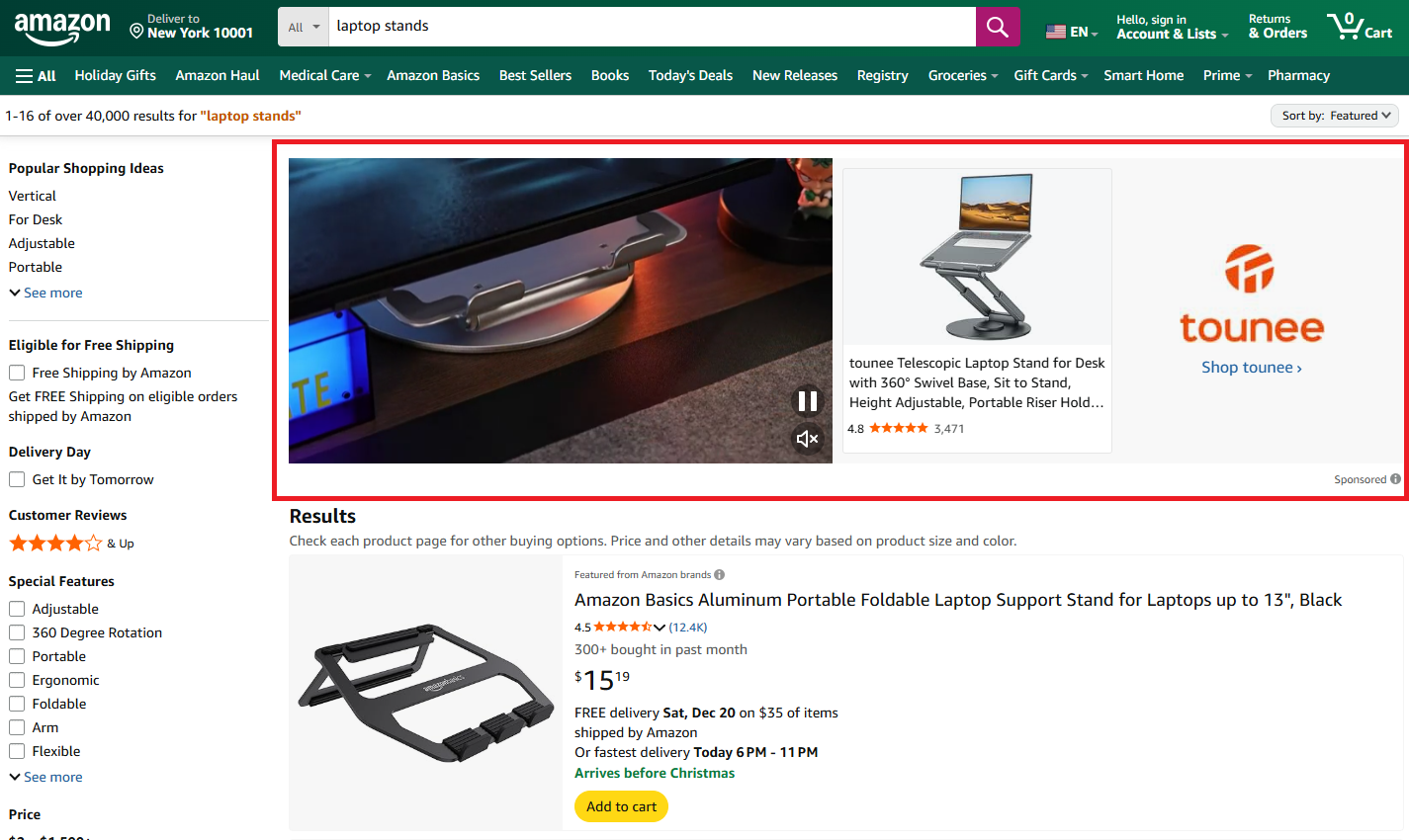
We can identify these by their cel_widget_id containing sb-video-product-collection-desktop. The brand name comes from the logo's alt text, and products are nested in carousel cards:
# Find top video ad widgets by their cel_widget_id
top_video_widgets = soup.find_all("div", {"cel_widget_id": lambda x: x and "sb-video-product-collection-desktop" in x})
for widget in top_video_widgets:
try:
# Extract brand name from the logo image alt text
brand_img = widget.find("img", alt=True)
brand_name = brand_img.get("alt", "") if brand_img else ""
# Extract headline text
headline_elem = widget.find("a", {"data-elementid": "sb-headline"})
headline = ""
if headline_elem:
truncate = headline_elem.find("span", class_="a-truncate-full")
headline = truncate.text.strip() if truncate else ""
# Extract products from the carousel
products = []
carousel_items = widget.find_all("li", class_="a-carousel-card")
for item in carousel_items:
asin_div = item.find("div", {"data-asin": True})
if asin_div and asin_div.get("data-asin"):
img = item.find("img")
products.append({
"asin": asin_div.get("data-asin"),
"image": img.get("src", "") if img else ""
})
sponsored_data["video_ads"].append({
"type": "top_featured",
"brand": brand_name,
"headline": headline,
"products": products
})
except Exception as e:
continue1.2. Mid-Search Video Ads
Single-product video ads appear between regular search results.
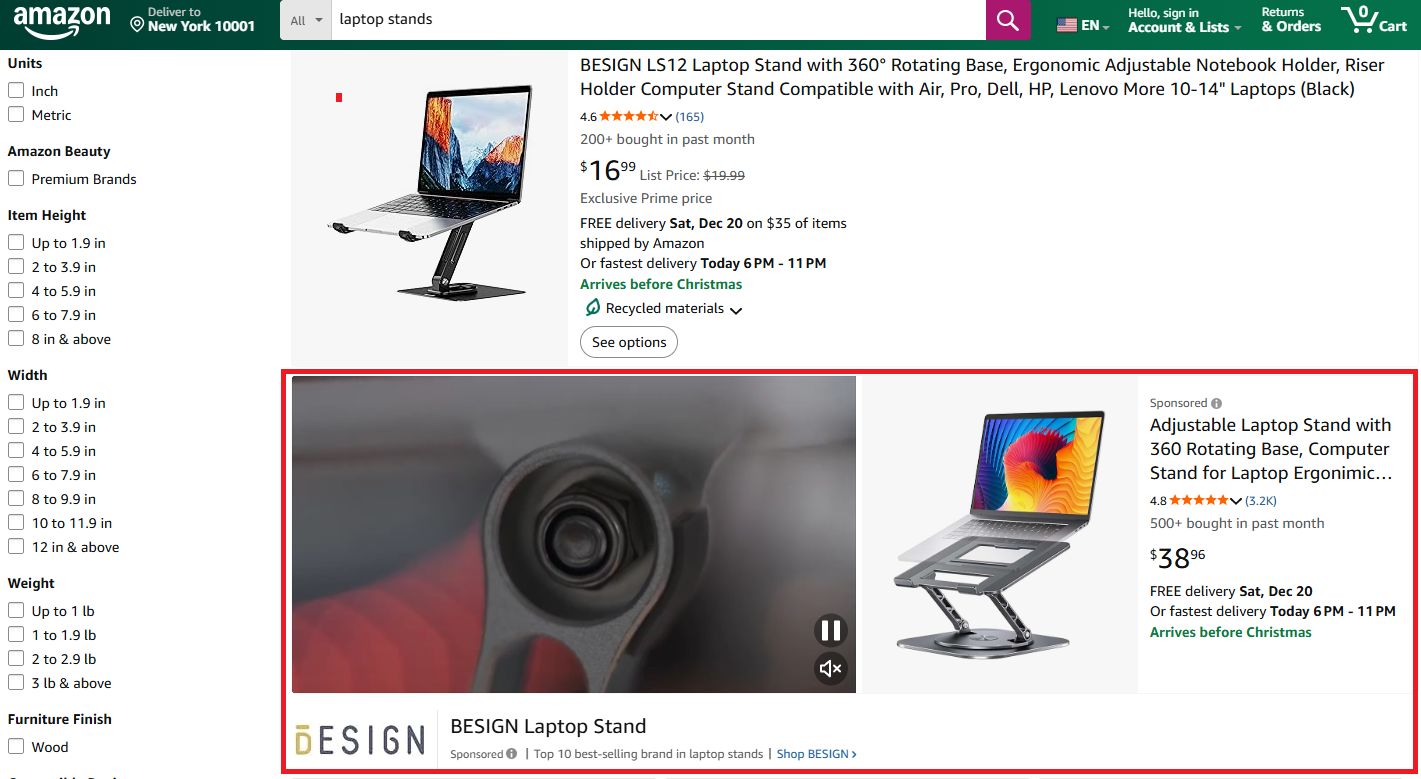
These have a VIDEO_SINGLE_PRODUCT class and store video URL and campaign metadata in a JSON data attribute. We parse the component props to extract video details and use regex to pull the ASIN from the product link:
# Find VIDEO_SINGLE_PRODUCT elements
video_single_products = soup.find_all("div", class_=lambda x: x and "VIDEO_SINGLE_PRODUCT" in x)
for video_item in video_single_products:
try:
# Parse the component props JSON for video details
component = video_item.find("span", {"data-component-type": "sbv-video-single-product"})
if component and component.get("data-component-props"):
props = json.loads(component["data-component-props"])
# Extract product link and ASIN from href
video_link = video_item.find("a", class_="sbv-desktop-video-link")
href = video_link.get("href", "") if video_link else ""
asin_match = re.search(r'/dp/([A-Z0-9]{10})', href)
sponsored_data["video_ads"].append({
"type": "video_single_product",
"video_url": props.get("videoSrc", ""),
"thumbnail": props.get("videoPreviewImageSrc", ""),
"asin": asin_match.group(1) if asin_match else "",
"campaign_id": props.get("campaignId", ""),
"ad_id": props.get("adId", ""),
"link": href
})
except Exception as e:
continue2. Extract In-Search Ads
These are sponsored products that appear inline with organic results—they look almost identical to regular listings but are marked "Sponsored."
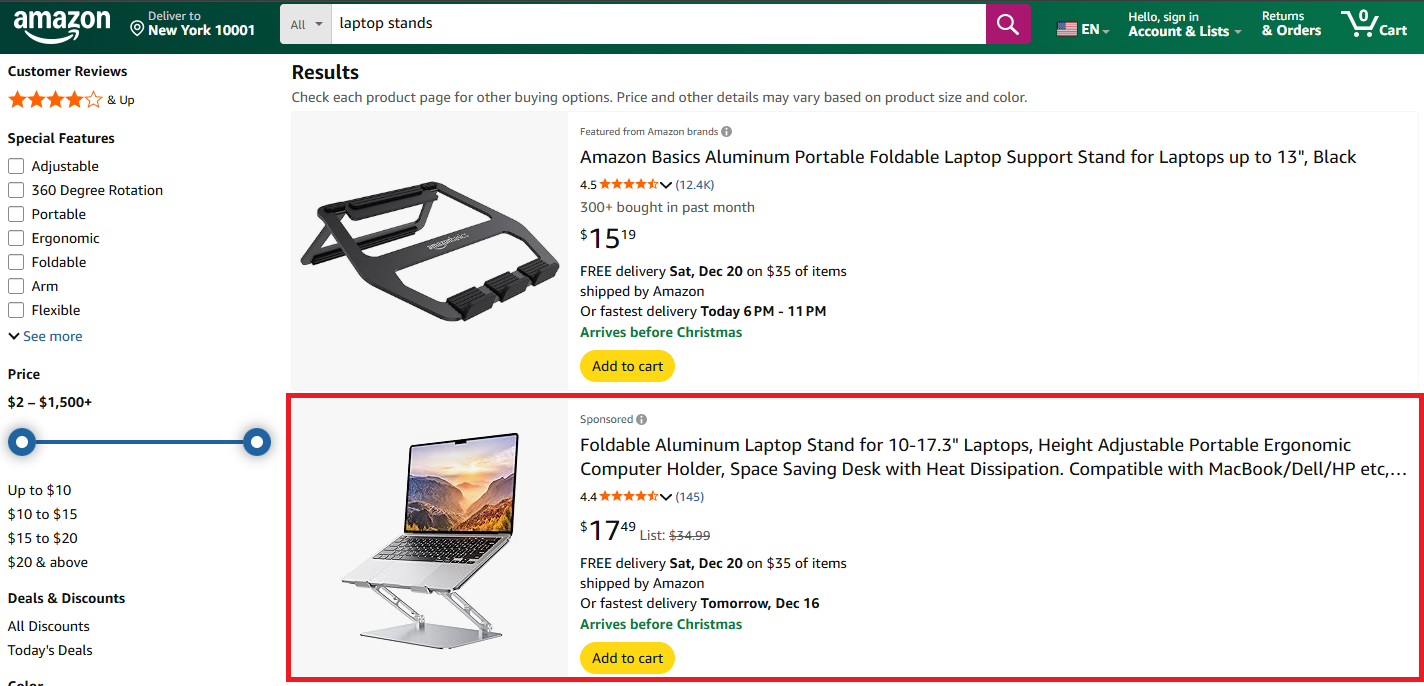
We identify them by the AdHolder class combined with a valid ASIN. The extraction logic mirrors what we used for regular products:
# Find all AdHolder elements with actual product ASINs
ad_holders = soup.find_all("div", class_=lambda x: x and "AdHolder" in x)
for ad in ad_holders:
asin = ad.get("data-asin", "")
# Only process if it has an ASIN and is a search result
if asin and ad.get("data-component-type") == "s-search-result":
try:
name_elem = ad.select_one("h2 span")
name = name_elem.text.strip() if name_elem else ""
# Price extraction (same method as regular products)
try:
price_elem = ad.select("span.a-price")
price = str(price_elem).split('a-offscreen">')[1].split('</span>')[0]
except:
price = "Price not available"
link_elem = ad.select_one(".a-link-normal")
link = link_elem.get("href", "") if link_elem else ""
img_elem = ad.select_one("img")
image = img_elem.get("src", "") if img_elem else ""
if name:
sponsored_data["in_search"].append({
"asin": asin,
"name": name,
"price": price,
"link": link,
"image": image
})
except Exception as e:
continue3. Extract Carousels
Brand carousels showcase multiple products from a single advertiser, appearing in dedicated slots with a brand logo and headline.
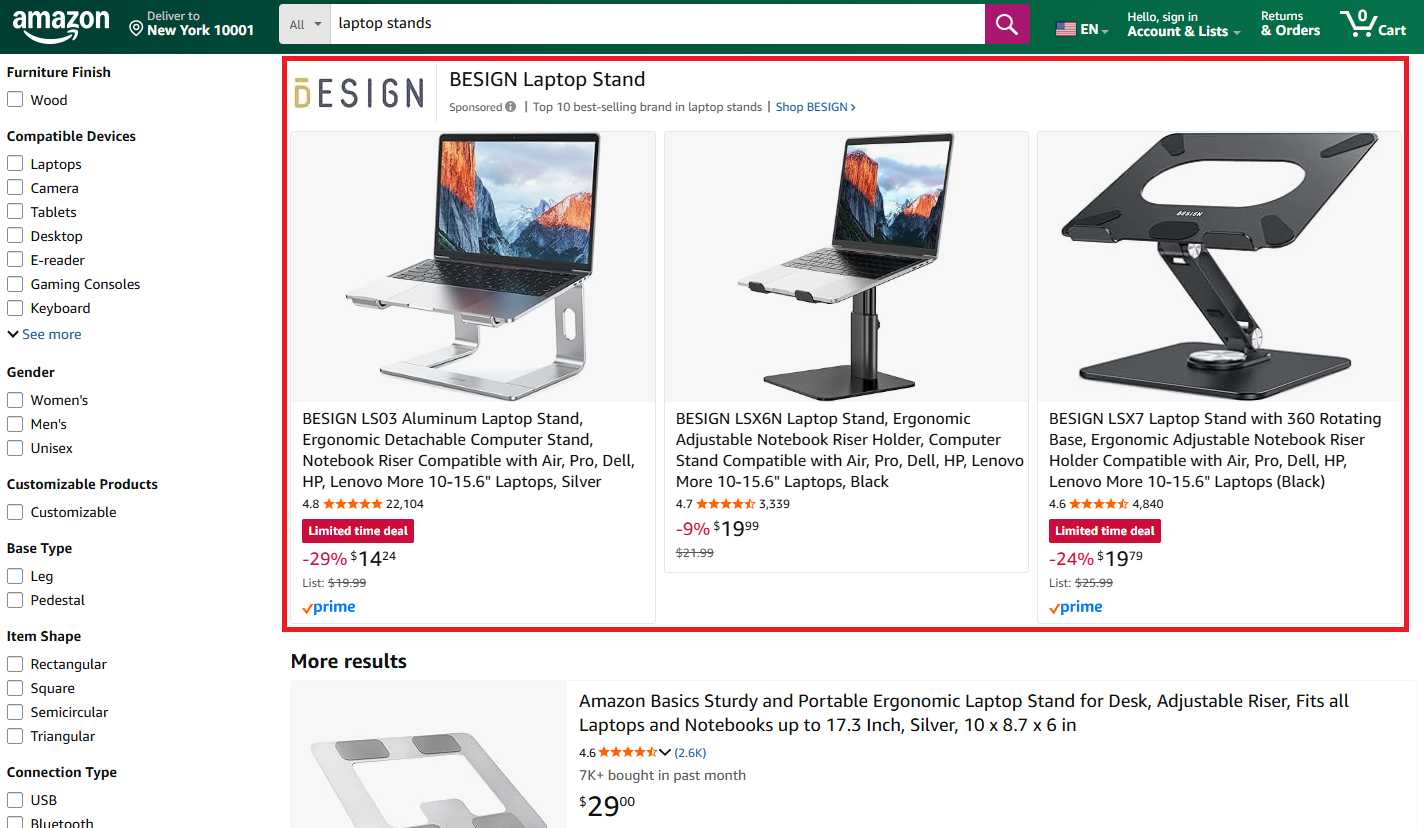
These are trickier to locate. We'll look for elements with sb-desktop in their class and CardInstance in their ID. Each carousel contains product cards with ASINs and images:
# Find themed collection carousels
themed_collections = soup.find_all("div", class_=lambda x: x and "sb-desktop" in str(x),
id=lambda x: x and "CardInstance" in str(x) if x else False)
# Fallback selector
if not themed_collections:
themed_collections = soup.find_all("div", {"data-slot": "desktop-inline"})
for collection in themed_collections:
try:
# Skip video single products (already captured above)
if "VIDEO_SINGLE_PRODUCT" in str(collection.get("class", [])):
continue
# Extract brand name from logo
brand_img = collection.find("img", alt=True)
brand_name = brand_img.get("alt") if brand_img and brand_img.get("alt") else ""
# Extract headline
headline_elem = collection.find("a", {"data-elementid": "sb-headline"})
headline = ""
if headline_elem:
truncate = headline_elem.find("span", class_="a-truncate-full")
headline = truncate.text.strip() if truncate else ""
# Extract products from carousel cards
products = []
carousel_items = collection.find_all("li", class_="a-carousel-card")
for item in carousel_items:
asin_div = item.find("div", {"data-asin": True})
if asin_div and asin_div.get("data-asin"):
img = item.find("img", alt=True)
products.append({
"asin": asin_div.get("data-asin"),
"name": img.get("alt", "") if img else "",
"image": img.get("src", "") if img else ""
})
if brand_name or products:
sponsored_data["carousels"].append({
"brand": brand_name,
"headline": headline,
"products": products
})
except Exception as e:
continue4. Extract Featured Brands
The "Brands related to your search" section displays brand cards that link to brand stores.
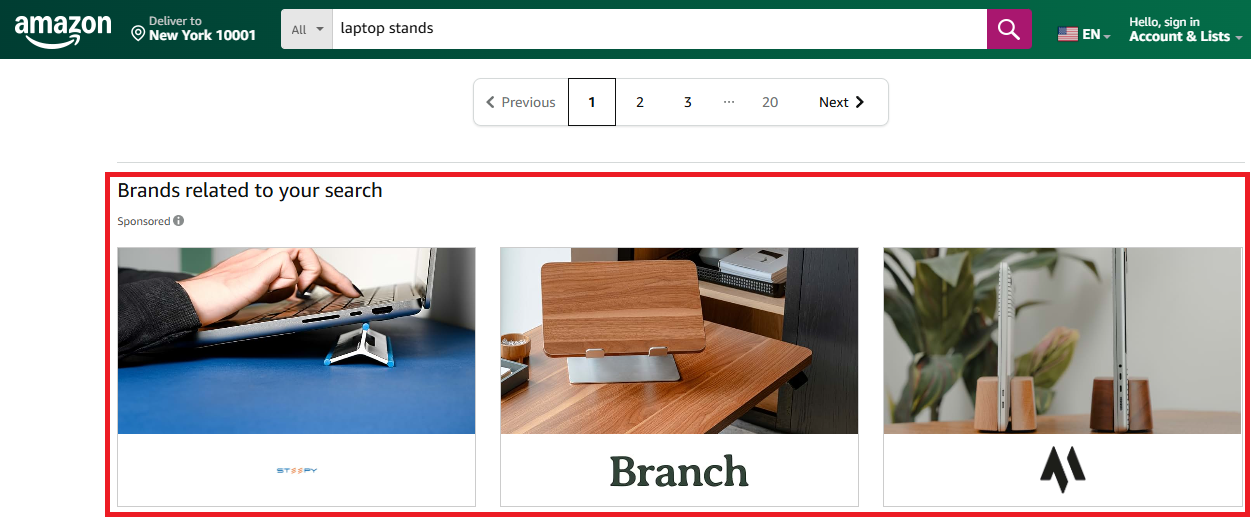
Amazon stores campaign data in a data-ad-creative-list JSON attribute, making extraction straightforward. We find the section by its cel_widget_id containing multi-brand-creative-desktop:
# Find multi-brand-creative sections
brand_sections = soup.find_all("div", {"cel_widget_id": lambda x: x and "multi-brand-creative-desktop" in x})
for section in brand_sections:
try:
# Extract brand data from the JSON attribute
ad_feedback = section.find("div", {"data-ad-creative-list": True})
if ad_feedback:
creative_list = json.loads(ad_feedback.get("data-ad-creative-list", "[]"))
for brand in creative_list:
brand_name = brand.get("title", "")
# Find the corresponding brand image
brand_img = section.find("img", alt=brand_name)
sponsored_data["featured_brands"].append({
"brand": brand_name,
"campaign_id": brand.get("campaignId", ""),
"ad_id": brand.get("adId", ""),
"image": brand_img.get("src", "") if brand_img else ""
})
except Exception as e:
continue5. Export to JSON
Finally, let's save all the sponsored data to a JSON file:
# Print summary
print("=== Sponsored Products Summary ===")
print(f"Video Ads: {len(sponsored_data['video_ads'])}")
print(f"In-Search Ads: {len(sponsored_data['in_search'])}")
print(f"Carousels: {len(sponsored_data['carousels'])}")
print(f"Featured Brands: {len(sponsored_data['featured_brands'])}")
# Export to JSON
output_file = "amazon_sponsored_products.json"
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(sponsored_data, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
print(f"\nData exported to {output_file}")If everything works as intended, your terminal should print this:
=== Sponsored Products Summary ===
Video Ads: 3
In-Search Ads: 8
Carousels: 2
Featured Brands: 4
Data exported to amazon_sponsored_products.jsonAnd amazon_sponsored_products.json should look like this:
Next Steps
We've mastered Amazon search: extracted product listings, related keywords, and competitor ads.
Keep scraping Amazon using these additional guides:
- Amazon scraping - Extract full product details, specifications, and seller information
- Scrape Amazon reviews - Collect customer reviews and ratings at scale
- Scrape Amazon best sellers - Monitor top-performing products by category
- Best Amazon scraper APIs - Compare tools for scraping Amazon at scale
Get 1000 free credits and start scraping Amazon with Scrape.do

Software Engineer