Category:Scraping Use Cases
How to Scrape Amazon Best Sellers with Python

Software Engineer
Amazon's Best Sellers page is as simple as that: whatever is selling the best right now.
So if you're in ecommerce, you need to start tracking ups and downs in the Best Sellers page to see what'll be the next top product.
In this guide, we'll do just that. Let's build a Python scraper that extracts the top 100 products from any Best Sellers category:
[All code available on GitHub] ⚙
What's Tricky About Scraping Best Seller Page on Amazon
The Best Sellers page isn't a simple HTML dump.
Amazon loads products dynamically as you scroll, which means a basic HTTP request only gets you part of the data.
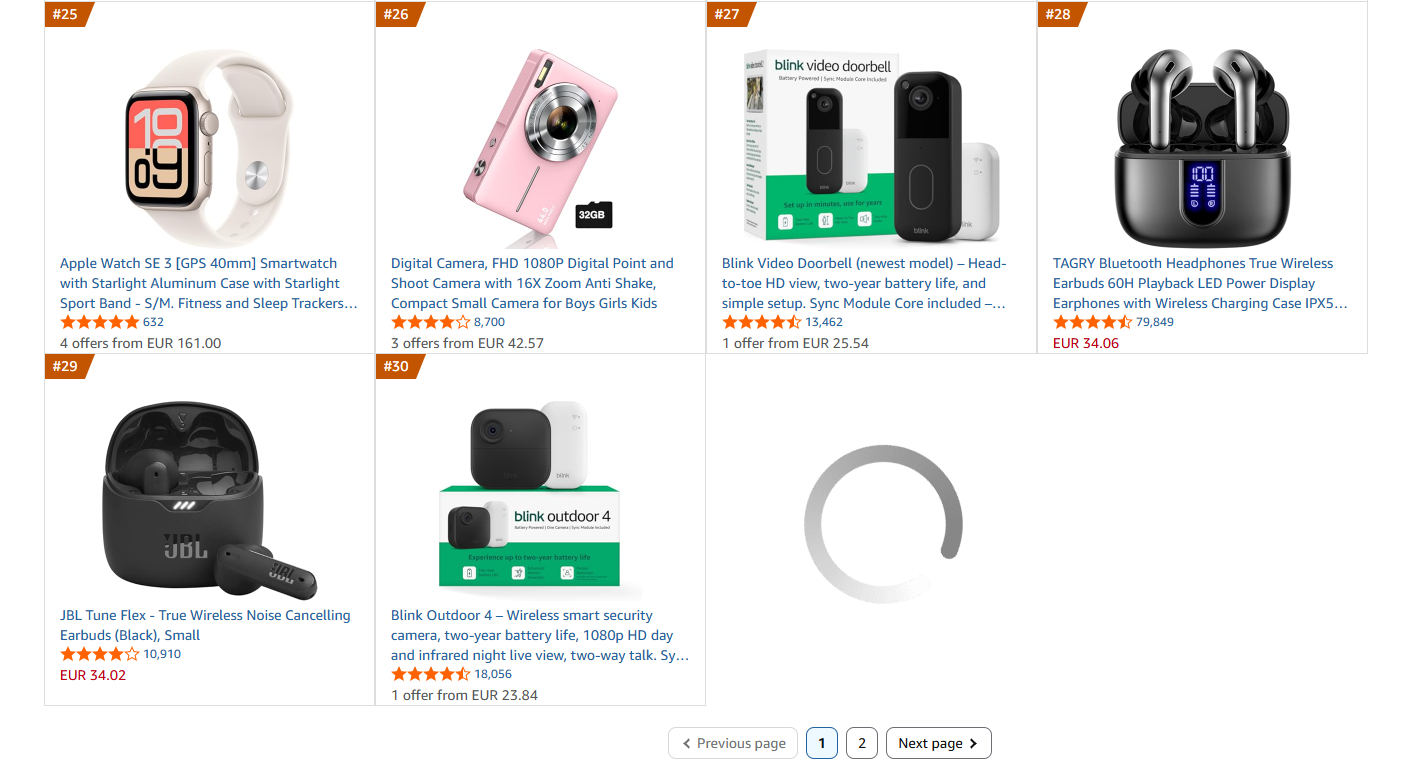
Only about 30 products load initially. The remaining 20 (to complete the top 50) only appear after scrolling down to the pagination area.
(Sometimes it loads up to 46, and you need to wait a second for the last 4 too!)
And unlike search results, the Best Sellers page requires JavaScript rendering.
The solution? We'll use Scrape.do's render and playWithBrowser parameters to scroll the page and trigger the lazy-loaded content before parsing.
Prerequisites
Before we start scraping, we need to:
Install Required Libraries
We'll use requests to send HTTP requests and beautifulsoup4 to parse the HTML:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4Grab a Free Scrape.do Token
Amazon uses AWS WAF to detect and block scrapers. For the Best Sellers page specifically, we also need JavaScript rendering to load all products.
We'll use Scrape.do to handle both; but the parsing logic in this guide works with any rendering solution.
To get your token, sign up here and grab it from the dashboard:

Scroll Down to Load Items
To load more products than the first 30, we need to simulate this scroll before parsing.
Scrape.do's playWithBrowser parameter lets us control the rendered browser with actions like clicking, scrolling, and waiting.
Here's our scroll sequence:
play_actions = [
{"Action": "ScrollTo", "Selector": ".a-pagination"},
{"Action": "Wait", "Timeout": 3000}
]This tells the browser to scroll down until the pagination element is visible, then wait 3 seconds for the lazy-loaded content to render.
Let's build the request:
import requests
import urllib.parse
import json
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Configuration
token = "<SDO-token>"
geocode = "us"
# Base URL for Electronics best sellers
base_url = "https://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics/zgbs/electronics/"
# playWithBrowser actions: scroll to pagination to load all 50 products
play_actions = [
{"Action": "ScrollTo", "Selector": ".a-pagination"},
{"Action": "Wait", "Timeout": 3000}
]
encoded_actions = urllib.parse.quote(json.dumps(play_actions))
# Build Scrape.do API URL with render and playWithBrowser
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote(base_url)
api_url = f"http://api.scrape.do/?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode={geocode}&render=true&playWithBrowser={encoded_actions}"
response = requests.get(api_url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")The key parameters are:
render=trueenables JavaScript renderingplayWithBrowserexecutes our scroll action before returning the HTMLgeoCode=usensures we get US-localized data
Loop Through the Second Page
Best Sellers shows 50 products per page. To get the full top 100, we need to scrape both pages.
Here's the catch: page 2 uses a different URL structure than page 1.
- Page 1:
https://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics/zgbs/electronics/ - Page 2:
https://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics/zgbs/electronics/ref=zg_bs_pg_2_electronics?_encoding=UTF8&pg=2
Let's wrap our request in a loop that handles both:
import requests
import urllib.parse
import json
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Configuration
token = "<SDO-token>"
geocode = "us"
max_pages = 2 # Best sellers shows 50 products per page, 2 pages = 100 products
# Base URL for Electronics best sellers
base_url = "https://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics/zgbs/electronics/"
# playWithBrowser actions: scroll to pagination to load all 50 products
play_actions = [
{"Action": "ScrollTo", "Selector": ".a-pagination"},
{"Action": "Wait", "Timeout": 3000}
]
encoded_actions = urllib.parse.quote(json.dumps(play_actions))
all_products = []
# Loop through pages
for page in range(1, max_pages + 1):
print(f"Scraping page {page}...")
# Build URL for current page
if page == 1:
target_url = base_url
else:
# Page 2+ URL format
target_url = f"{base_url}ref=zg_bs_pg_{page}_electronics?_encoding=UTF8&pg={page}"
# Build Scrape.do API URL with render and playWithBrowser
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote(target_url)
api_url = f"http://api.scrape.do/?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode={geocode}&render=true&playWithBrowser={encoded_actions}"
response = requests.get(api_url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")The same playWithBrowser scroll action works for both pages, we just change the target URL.
Parse Product Rankings and Information
Now for the fun part (maybe): extracting product data from the HTML.
Each product on the Best Sellers page sits inside an element with the class zg-no-numbers. From there, we can extract:
- Ranking – The product's position (1-50 per page)
- ASIN – Amazon's unique product identifier, found in
data-asin - Name & Link – From the anchor tag with class
a-link-normal - Price – From the span with class
p13n-sc-price - Rating & Review Count – Stored in the
aria-labelattribute of the star rating element - Image – From the
imgtag
Here's the entire parsing logic:
# Find all product items
product_items = soup.find_all(class_="zg-no-numbers")
for index, item in enumerate(product_items, start=1):
try:
# RANKING: Position in the list (1-50 per page)
ranking = str(index + (page - 1) * 50)
# ASIN: From data-asin attribute on child element
asin_elem = item.find(attrs={"data-asin": True})
asin = asin_elem.get("data-asin", "") if asin_elem else ""
# IMAGE: Get src from img tag
img_tag = item.find("img")
image = img_tag.get("src", "") if img_tag else ""
# NAME & LINK: From anchor with class "a-link-normal" containing "/dp/"
name = ""
link = ""
for a_tag in item.find_all("a", class_="a-link-normal"):
href = a_tag.get("href", "")
text = a_tag.get_text(strip=True)
# The product link contains "/dp/" and has the product name as text
if "/dp/" in href and text and not text.startswith("$"):
link = "https://www.amazon.com" + href if not href.startswith("http") else href
name = text
break
# PRICE: From span with class containing "p13n-sc-price"
price_tag = item.find("span", class_=lambda x: x and "p13n-sc-price" in str(x))
price = price_tag.get_text(strip=True) if price_tag else "Price not available"
# RATING & REVIEW COUNT: From aria-label on the anchor containing star icon
rating = ""
review_count = ""
star_icon = item.find("i", class_=lambda x: x and "a-icon-star" in str(x))
if star_icon:
parent_link = star_icon.find_parent("a")
if parent_link:
aria_label = parent_link.get("aria-label", "")
# aria-label format: "4.5 out of 5 stars, 12,345 ratings"
if aria_label and "stars" in aria_label:
parts = aria_label.split("stars")
rating = parts[0].strip() + " stars" if parts[0] else ""
if len(parts) > 1:
review_part = parts[1].strip().lstrip(",").strip()
review_count = review_part.replace(" ratings", "")
if name:
all_products.append({
"Ranking": ranking,
"ASIN": asin,
"Name": name,
"Price": price,
"Rating": rating,
"Review Count": review_count,
"Link": link,
"Image": image
})
except Exception as e:
continue
print(f" Found {len(product_items)} products on page {page}")A few things to note:
The rating and review count are packed into a single aria-label string like "4.5 out of 5 stars, 12,345 ratings". We split on "stars" rather than comma to avoid breaking on thousand separators in the review count.
The name extraction filters out anchor tags that contain prices (starting with "$") since some product cards have multiple a-link-normal elements.
Export to CSV
Let's put it all together and export to CSV. Here's the complete script:
import requests
import urllib.parse
import json
import csv
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Configuration
token = "<SDO-token>"
geocode = "us"
max_pages = 2 # Best sellers shows 50 products per page, 2 pages = 100 products
# Base URL for Electronics best sellers
base_url = "https://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics/zgbs/electronics/"
# playWithBrowser actions: scroll to pagination to load all 50 products
play_actions = [
{"Action": "ScrollTo", "Selector": ".a-pagination"},
{"Action": "Wait", "Timeout": 3000}
]
encoded_actions = urllib.parse.quote(json.dumps(play_actions))
all_products = []
# Loop through pages
for page in range(1, max_pages + 1):
print(f"Scraping page {page}...")
# Build URL for current page
if page == 1:
target_url = base_url
else:
# Page 2+ URL format
target_url = f"{base_url}ref=zg_bs_pg_{page}_electronics?_encoding=UTF8&pg={page}"
# Build Scrape.do API URL with render and playWithBrowser
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote(target_url)
api_url = f"http://api.scrape.do/?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode={geocode}&render=true&playWithBrowser={encoded_actions}"
response = requests.get(api_url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
# Find all product items - each one has the class "zg-no-numbers"
product_items = soup.find_all(class_="zg-no-numbers")
for index, item in enumerate(product_items, start=1):
try:
# RANKING: Position in the list (1-50 per page)
ranking = str(index + (page - 1) * 50)
# ASIN: From data-asin attribute on child element
asin_elem = item.find(attrs={"data-asin": True})
asin = asin_elem.get("data-asin", "") if asin_elem else ""
# IMAGE: Get src from img tag
img_tag = item.find("img")
image = img_tag.get("src", "") if img_tag else ""
# NAME & LINK: From anchor with class "a-link-normal" containing "/dp/" and text
name = ""
link = ""
for a_tag in item.find_all("a", class_="a-link-normal"):
href = a_tag.get("href", "")
text = a_tag.get_text(strip=True)
# The product link contains "/dp/" and has the product name as text
if "/dp/" in href and text and not text.startswith("EUR") and not text.startswith("$"):
link = "https://www.amazon.com" + href if not href.startswith("http") else href
name = text
break
# PRICE: From span with class containing "p13n-sc-price"
price_tag = item.find("span", class_=lambda x: x and "p13n-sc-price" in str(x))
price = price_tag.get_text(strip=True) if price_tag else "Price not available"
# RATING & REVIEW COUNT: From aria-label on the anchor containing star icon
rating = ""
review_count = ""
star_icon = item.find("i", class_=lambda x: x and "a-icon-star" in str(x))
if star_icon:
parent_link = star_icon.find_parent("a")
if parent_link:
aria_label = parent_link.get("aria-label", "")
# aria-label format: "4.5 out of 5 stars, 12,345 ratings"
if aria_label and "stars" in aria_label:
# Split after "stars" to avoid splitting on thousands separator
parts = aria_label.split("stars")
rating = parts[0].strip() + " stars" if parts[0] else ""
if len(parts) > 1:
# Remove leading comma and " ratings" suffix
review_part = parts[1].strip().lstrip(",").strip()
review_count = review_part.replace(" ratings", "")
if name:
all_products.append({
"Ranking": ranking,
"ASIN": asin,
"Name": name,
"Price": price,
"Rating": rating,
"Review Count": review_count,
"Link": link,
"Image": image
})
except Exception as e:
continue
print(f" Found {len(product_items)} products on page {page}")
# Export to CSV
csv_file = "amazon_best_sellers.csv"
headers = ["Ranking", "ASIN", "Name", "Price", "Rating", "Review Count", "Link", "Image"]
with open(csv_file, "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as file:
writer = csv.DictWriter(file, fieldnames=headers)
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(all_products)
print(f"\nTotal products scraped: {len(all_products)}")
print(f"Data successfully exported to {csv_file}")Run it, and you'll see:
Scraping page 1...
Found 50 products on page 1
Scraping page 2...
Found 50 products on page 2
Total products scraped: 100
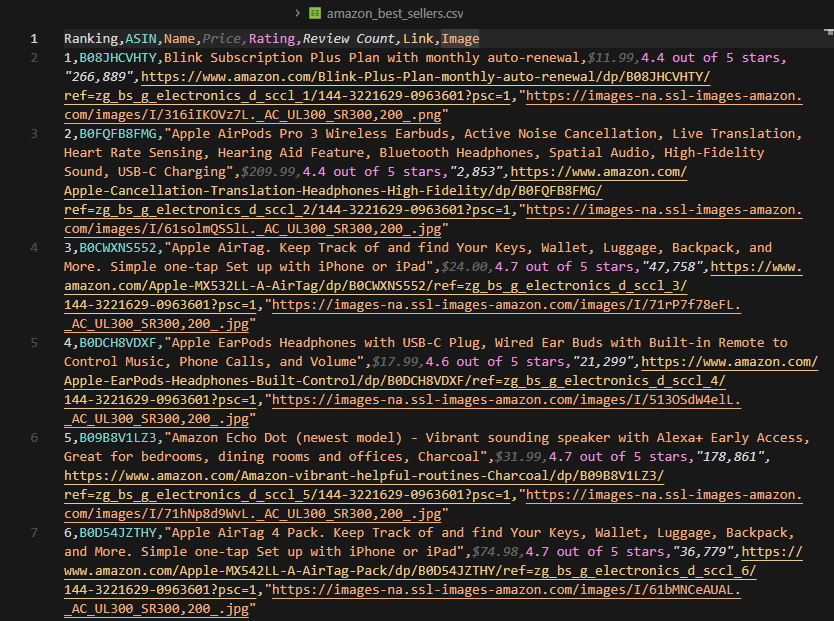
Data successfully exported to amazon_best_sellers.csvYour CSV will contain all 100 best-selling products with rankings, prices, ratings, and review counts—ready for analysis or import into your product research tools.
Next Steps
Now that you can scrape Best Sellers rankings, keep scraping other data from Amazon:
- Amazon scraping - Extract full product details, specifications, and seller information
- Scrape Amazon search - Extract product listings, related searches, and sponsored ads
- Scrape Amazon reviews - Collect customer reviews and ratings at scale
- Best Amazon scraper APIs - Compare tools for scraping Amazon at scale
Get 1000 free credits and start scraping Amazon with Scrape.do

Software Engineer