Category:Scraping Use Cases
Scraping Etsy Product Data, Categories, and Reviews with Python

Software Engineer
Etsy is the #1 website for selling arts and crafts with millions of unique handmade and vintage products.
But scraping it is harder than your average e-com platform.
Etsy sits behind DataDome's bot protection, blocks most proxy services instantly, and geo-restricts data based on your IP location. Most scrapers fail before they can pull a single product listing.
In this guide, we'll bypass those obstacles and scrape product details from Etsy using Python and Scrape.do.
Find the complete working code on GitHub ⚙
Why Is Scraping Etsy Difficult?
Etsy doesn't make it easy to extract data programmatically.
Between heavy bot detection and IP-based filtering, you'll need more than basic requests and free proxies to pull product information at scale.
DataDome Protection
Etsy is protected by DataDome, one of the most aggressive anti-bot systems available.
They're proud of it too; Etsy even has a public success story on DataDome's site highlighting how they block unwanted traffic and reduce computing costs.
DataDome analyzes your TLS fingerprint, browser behavior, mouse movements, and request patterns. If anything looks automated, you're blocked instantly with a challenge page or a hard 403.
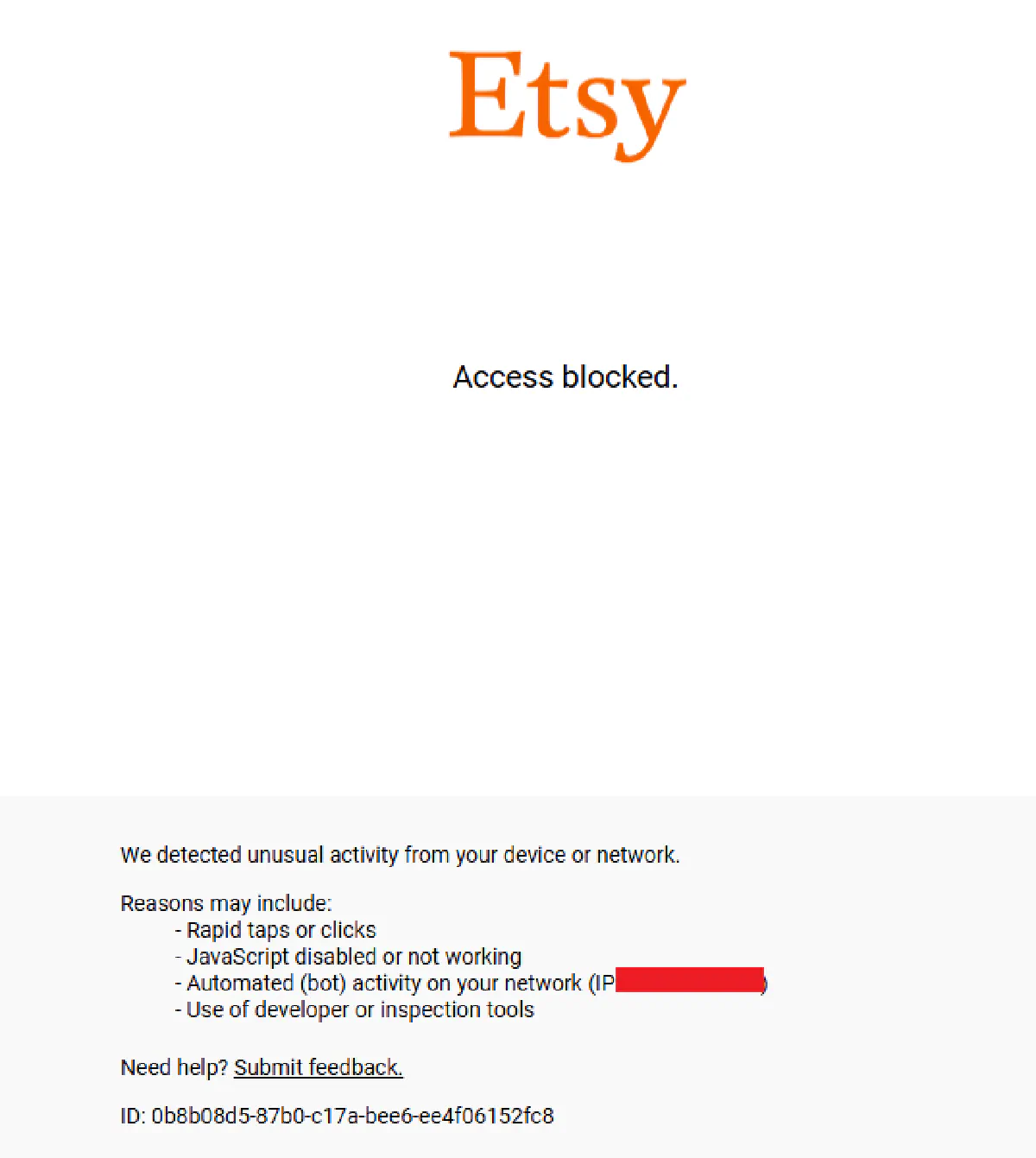
This means simple Python requests won't work, and most headless browser setups get flagged within seconds.
Basic Proxies Provide Limited Access
Free or low-quality proxies aren't completely blocked by Etsy, but they won't get you far either.
You can usually access the homepage and browse category pages with datacenter IPs, but the moment you try to scrape search results tailored to a specific country or load product pages with pricing and shipping details, you'll hit a wall.
For reliable access to product data, reviews, and localized pricing, you need high-quality residential proxies that mimic real user traffic from the target region.
How Scrape.do Bypasses Etsy
Scrape.do handles Etsy's defenses by:
- Rotating residential proxies from real ISPs to avoid DataDome fingerprinting
- Spoofing TLS fingerprints to pass bot detection checks
- Managing sessions automatically so requests appear as organic browsing behavior
- Geo-targeting requests with
geoCodeto access location-specific pricing and availability
This means you send a single API request and get clean HTML back, without worrying about blocks or proxy rotation.
Scrape Product Data from Etsy Product Pages
We'll scrape this handmade wooden sign listing and extract all the product details embedded in its structured data.
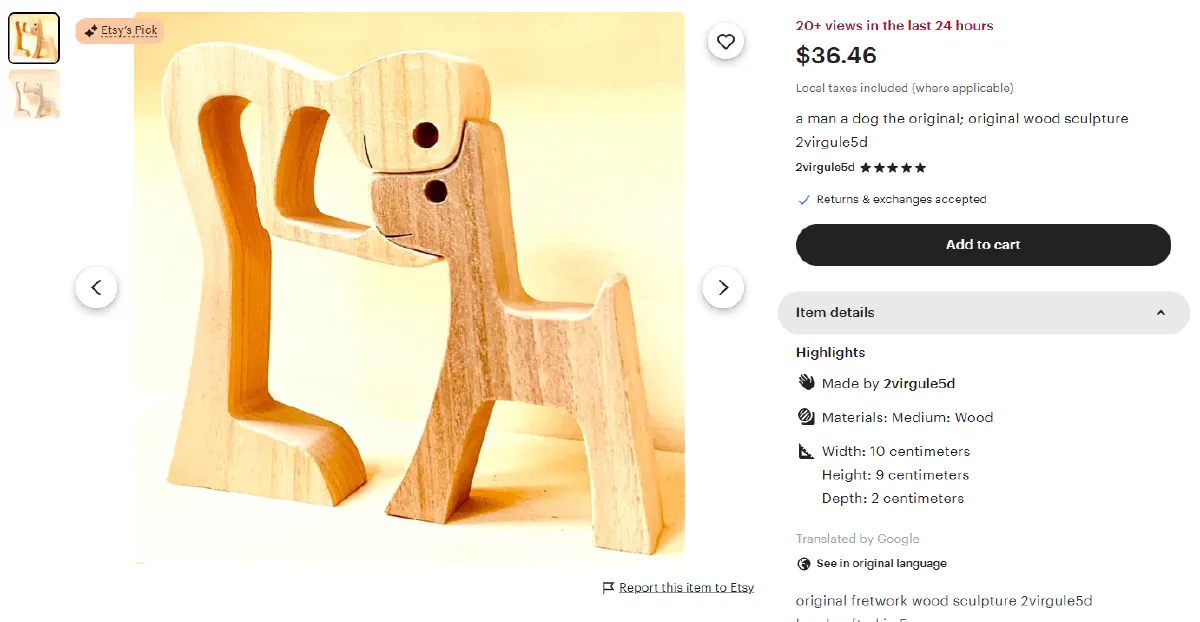
Etsy embeds full product information inside JSON-LD schema blocks in the HTML. This makes scraping much cleaner than parsing individual DOM elements, because the data is already structured and ready to parse.
We'll extract:
- Product name and description
- Shop/brand name
- Category
- Images
- Price and currency
- Availability
- Rating and review count
Setup and Prerequisites
Before we start scraping, we need to install the required libraries and set up our Scrape.do API credentials.
Install the necessary Python packages:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4These libraries handle HTTP requests and HTML parsing.
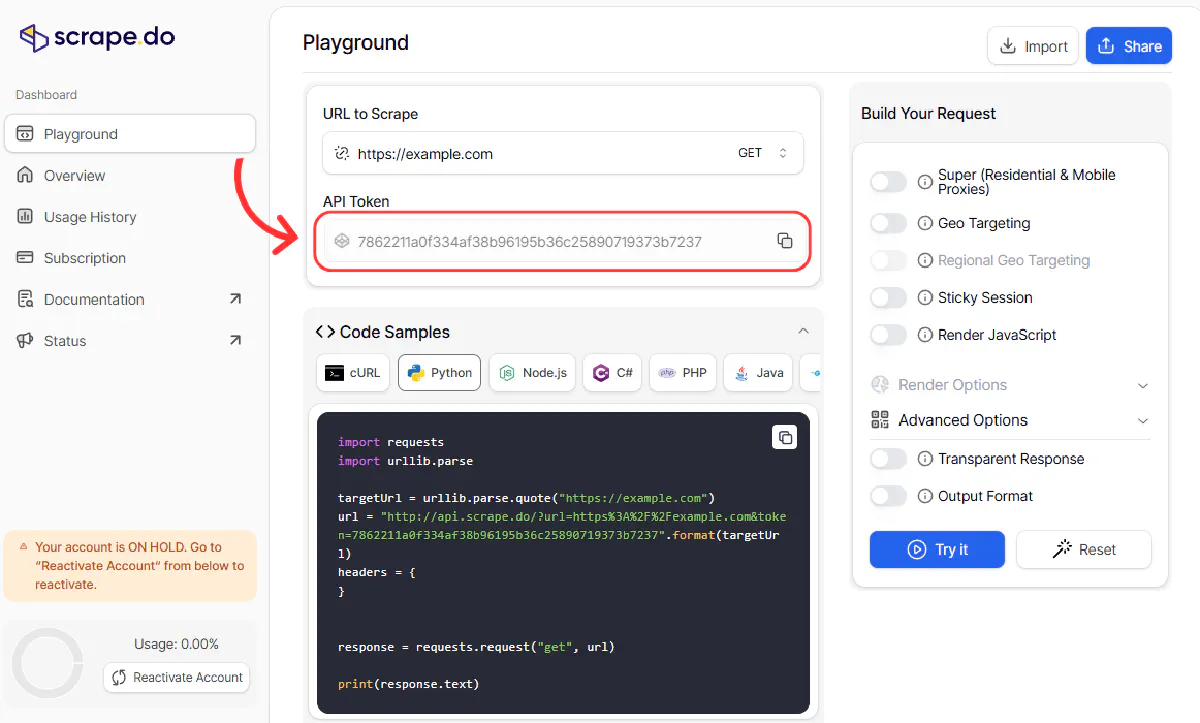
Next, sign up at Scrape.do to get your API token. You'll get 1000 free credits every month to start scraping immediately.
Once you're logged in, copy your token from the top of the dashboard:
Now we'll build the request to fetch the product page. We're using super=true for premium residential proxies, geoCode=us to get US-specific pricing and shipping details.
We're also passing
"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"as extra headers created specifically for Etsy through Scrape.do.
import requests
import urllib.parse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import json
import re
# Configuration
token = "<your-token>"
product_url = "https://www.etsy.com/listing/468670752/a-man-a-dog-the-original-original-wood"
# Make API request
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(product_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode=us&super=true&extraHeaders=true"
headers = {"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"}
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")This sends the request through Scrape.do's infrastructure, bypassing DataDome and returning the fully rendered HTML. The extraHeaders parameter ensures our custom locale header is included in the request.
Extract Product Data from JSON
Etsy includes structured product data inside <script type="application/ld+json"> tags using JSON-LD format. We'll parse these blocks to extract all the details we need.
Start by initializing a product dictionary and extracting the listing ID from the URL:
# Initialize product data
product = {"url": product_url}
# Extract listing ID from URL
listing_match = re.search(r"/listing/(\d+)", product_url)
if listing_match:
product["listing_id"] = listing_match.group(1)The listing ID is useful for tracking products or building URLs programmatically later.
Find JSON-LD Script Tags
Etsy embeds multiple JSON-LD blocks in the page. We need to find the one with "@type": "Product":
# Extract JSON-LD structured data
for script in soup.find_all("script", attrs={"type": "application/ld+json"}):
try:
data = json.loads(script.string)
objs = data if isinstance(data, list) else [data]
for obj in objs:
product_type = obj.get("@type")
if product_type == "Product" or (isinstance(product_type, list) and "Product" in product_type):This loop finds all JSON-LD scripts, parses them, and checks if they contain product data. Some pages have multiple schema objects, so we handle both single objects and arrays.
Extract Name, Description, and Category
Once we've found the Product object, we extract basic product information:
# Extract basic info
product["name"] = obj.get("name")
product["description"] = obj.get("description")
product["category"] = obj.get("category")These fields give us the product title, full description, and the category it's listed under.
Extract Shop/Brand Name
The shop name is stored in the brand field, which can be either a string or a dictionary:
# Extract shop/brand
brand = obj.get("brand")
if isinstance(brand, dict):
product["shop"] = brand.get("name")
elif isinstance(brand, str):
product["shop"] = brandWe check the type and extract the name accordingly. This gives us the seller's shop name.
Extract Images
Product images are stored in the image field, which can be a single URL or an array of URLs:
# Extract images
image_data = obj.get("image")
if isinstance(image_data, list):
product["images"] = image_data
elif image_data:
product["images"] = [image_data]
else:
product["images"] = []We normalize this into a list format so downstream code always gets an array of image URLs.
Extract Price and Currency
Price information lives inside the offers object. Etsy sometimes uses price or lowPrice depending on whether there are variations:
# Extract price from offers
offers = obj.get("offers")
if isinstance(offers, list):
offers = offers[0] if offers else {}
price = (offers or {}).get("price") or (offers or {}).get("lowPrice")
product["price"] = float(price) if price else None
product["currency"] = (offers or {}).get("priceCurrency")This captures the price as a float and the currency code (like "USD").
Extract Availability
The availability field tells us if the product is in stock:
# Extract availability
avail = (offers or {}).get("availability") or ""
if "/" in avail:
product["availability"] = avail.split("/")[-1]
elif avail:
product["availability"] = availIf the availability value contains a slash, we take the last part; otherwise we use the value as-is.
Extract Rating and Review Count
Finally, we pull the aggregate rating data:
# Extract rating
agg = obj.get("aggregateRating") or {}
product["rating"] = agg.get("ratingValue")
product["review_count"] = agg.get("reviewCount")
break
except:
continue
# Print results
print(json.dumps(product, indent=2, sort_keys=True))This gives us the average star rating and total number of reviews, completing our product data extraction.
Running Full Code
Here's the complete script that extracts all product data from an Etsy listing:
import requests
import urllib.parse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import json
import re
# Configuration
token = "<your-token>"
product_url = "https://www.etsy.com/listing/468670752/a-man-a-dog-the-original-original-wood"
# Make API request
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(product_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode=us&super=true&extraHeaders=true"
headers = {"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"}
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
# Initialize product data
product = {"url": product_url}
# Extract listing ID from URL
listing_match = re.search(r"/listing/(\d+)", product_url)
if listing_match:
product["listing_id"] = listing_match.group(1)
# Extract JSON-LD structured data
for script in soup.find_all("script", attrs={"type": "application/ld+json"}):
try:
data = json.loads(script.string)
objs = data if isinstance(data, list) else [data]
for obj in objs:
product_type = obj.get("@type")
if product_type == "Product" or (isinstance(product_type, list) and "Product" in product_type):
# Extract basic info
product["name"] = obj.get("name")
product["description"] = obj.get("description")
product["category"] = obj.get("category")
# Extract shop/brand
brand = obj.get("brand")
if isinstance(brand, dict):
product["shop"] = brand.get("name")
elif isinstance(brand, str):
product["shop"] = brand
# Extract images
image_data = obj.get("image")
if isinstance(image_data, list):
product["images"] = image_data
elif image_data:
product["images"] = [image_data]
else:
product["images"] = []
# Extract price from offers
offers = obj.get("offers")
if isinstance(offers, list):
offers = offers[0] if offers else {}
price = (offers or {}).get("price") or (offers or {}).get("lowPrice")
product["price"] = float(price) if price else None
product["currency"] = (offers or {}).get("priceCurrency")
# Extract availability
avail = (offers or {}).get("availability") or ""
if "/" in avail:
product["availability"] = avail.split("/")[-1]
elif avail:
product["availability"] = avail
# Extract rating
agg = obj.get("aggregateRating") or {}
product["rating"] = agg.get("ratingValue")
product["review_count"] = agg.get("reviewCount")
break
except:
continue
# Print results
print(json.dumps(product, indent=2, sort_keys=True))When you run this script, you'll get structured JSON output with all the extracted data:
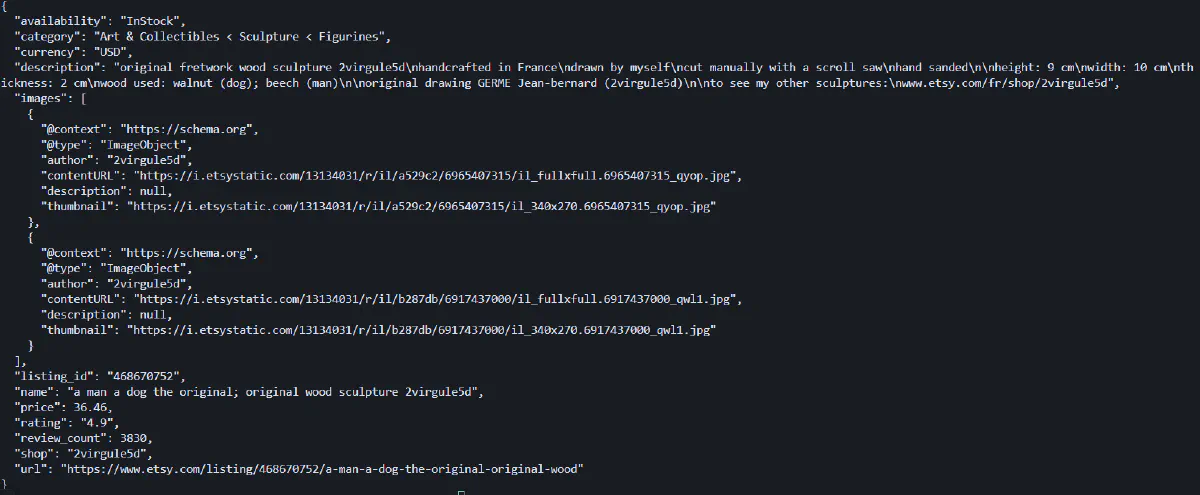
Scrape Etsy Reviews
Product reviews are the best way to find the products that are loved, or hated, by the consumer.
So obviously, we need to scrape that too.
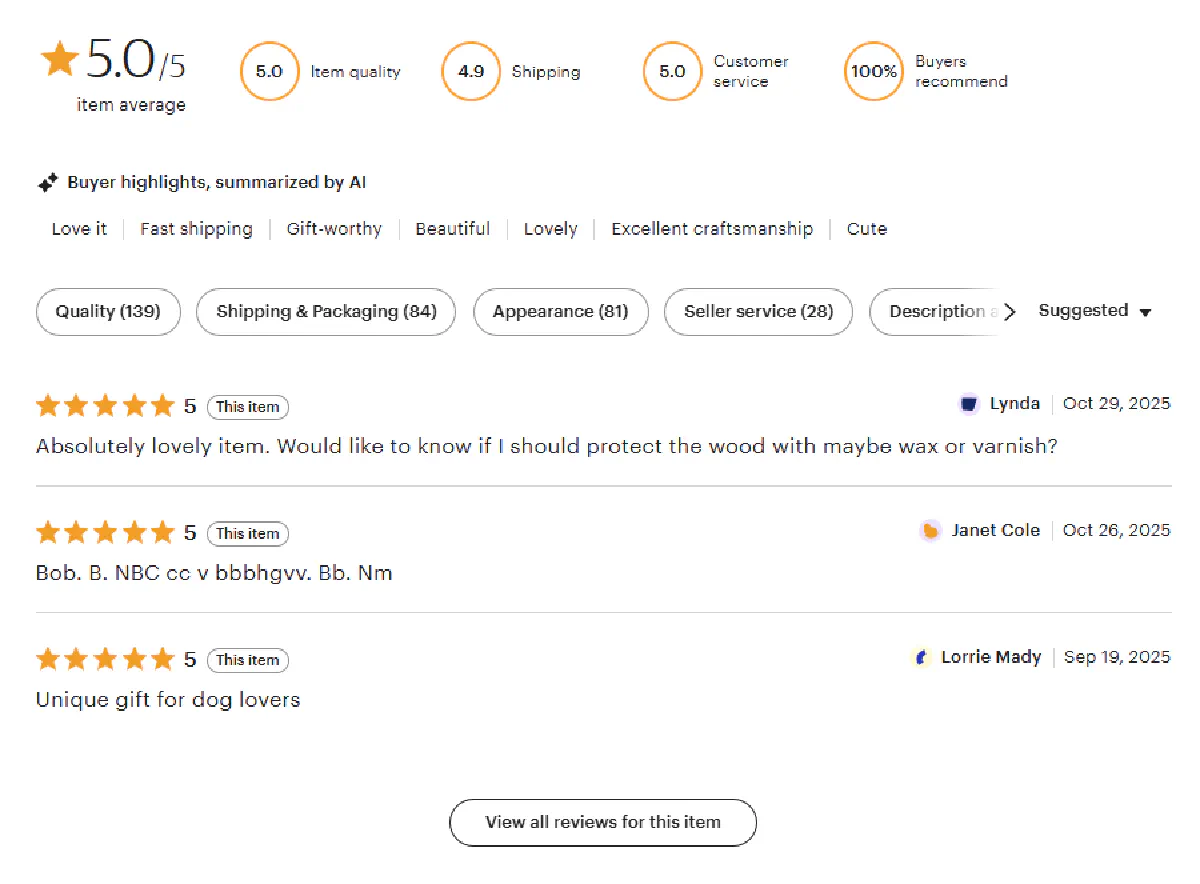
But unlike product details which are embedded in the page HTML, reviews are loaded dynamically through Etsy's internal GraphQL API after the page loads.
We'll extract reviews by making POST requests to Etsy's review endpoint with the proper payload structure and authentication tokens.
Finding the Reviews API Endpoint
Before we start coding, let's find the API endpoint that Etsy uses to load reviews. Open any product page in Chrome and open Developer Tools (F12). Go to the Network tab and filter by "Fetch/XHR". Then scroll down to the reviews section on the page.
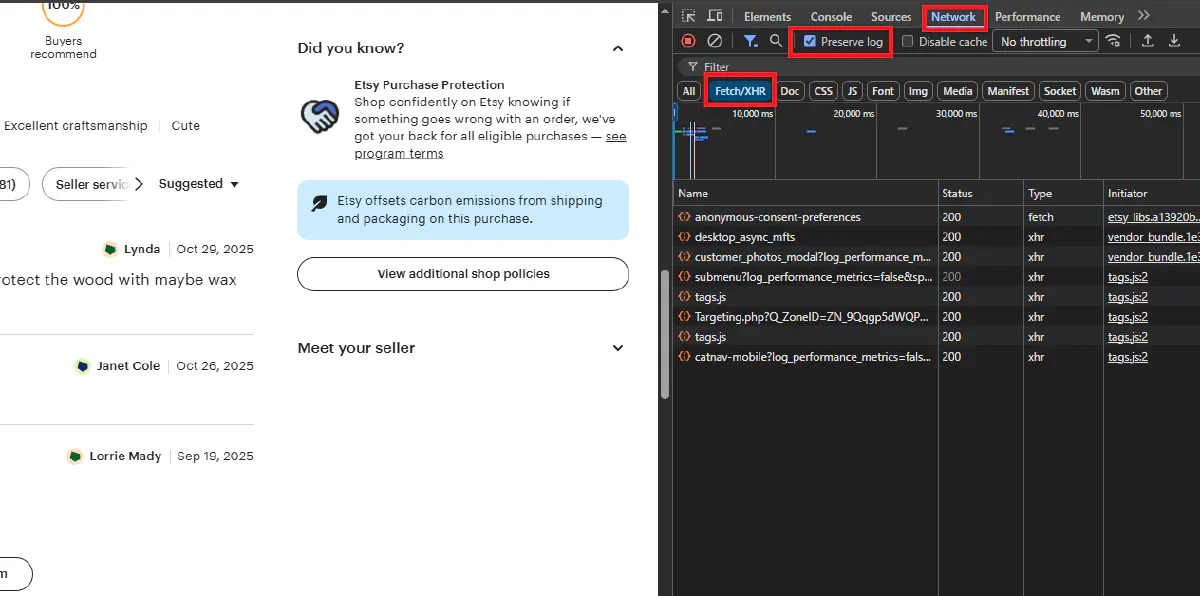
You'll see POST requests to deep_dive_reviews. Click on one to inspect it.
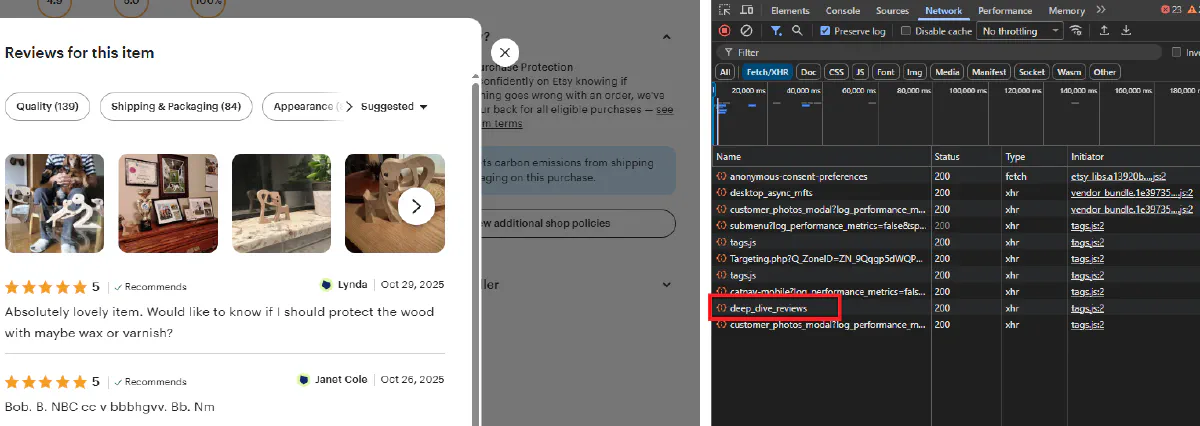
In the Payload tab, you can see the request structure with listing_id, shop_id, and page parameters:
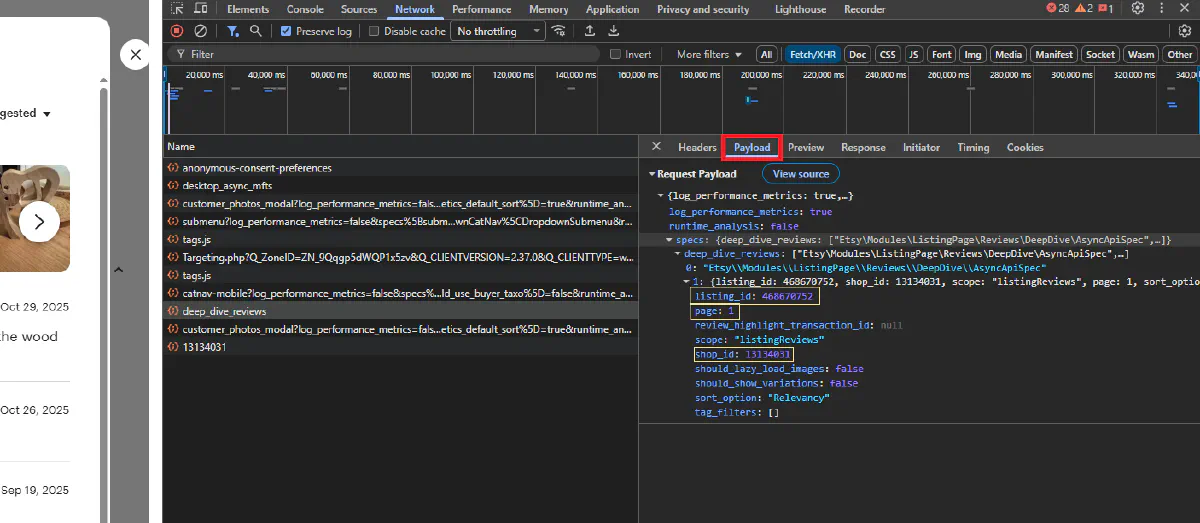
And in the Response tab, you'll see HTML fragments containing the review cards:
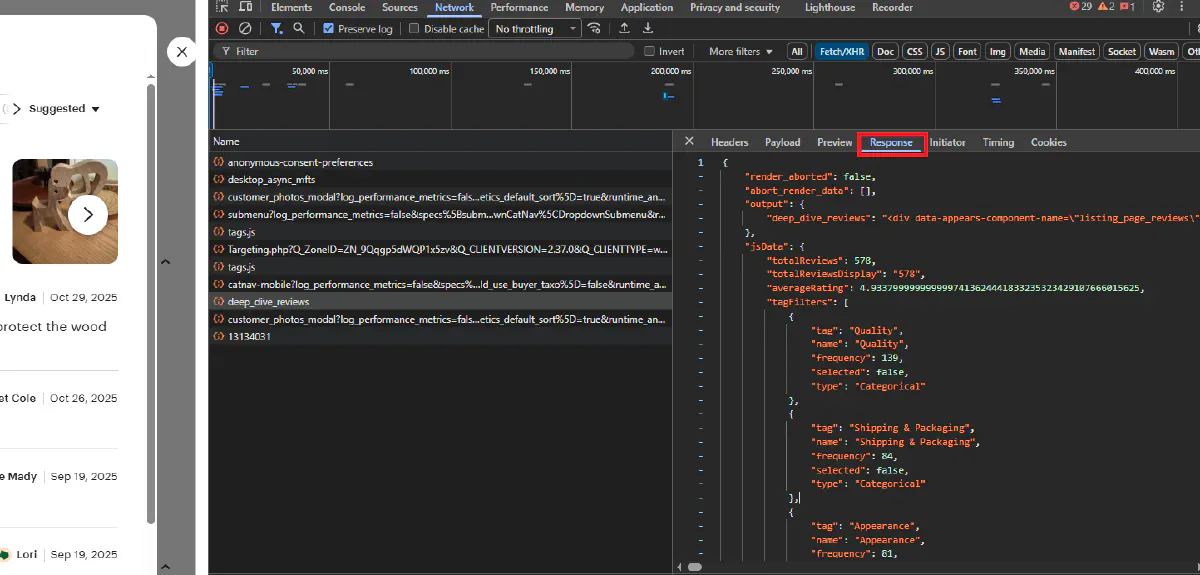
Now that we understand the structure, let's build our scraper.
Extract Required IDs and CSRF Token
Before we can fetch reviews, we need three pieces of information from the product page:
- Listing ID - The product identifier from the URL
- Shop ID - The seller's shop identifier
- CSRF Token - An anti-forgery token required by Etsy's API
Start by fetching the product page and extracting these values:
import requests
import urllib.parse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import json
import re
import time
# Configuration
token = "<your-token>"
product_url = "https://www.etsy.com/listing/468670752/a-man-a-dog-the-original-original-wood"
max_pages = 5
sort_option = "Relevancy" # Options: "Relevancy", "MostRecent", "MostHelpful"
# Fetch product page to extract IDs and CSRF token
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(product_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode=us&super=true&extraHeaders=true"
headers = {"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"}
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers)
html = response.textThis fetches the product page through Scrape.do, which bypasses DataDome and returns the full HTML.
Extract Listing ID
The listing ID is in the URL path:
# Extract listing ID
listing_id = None
listing_match = re.search(r"/listing/(\d+)", product_url)
if listing_match:
listing_id = int(listing_match.group(1))
else:
listing_match = re.search(r'/listing/(\d+)', html)
if listing_match:
listing_id = int(listing_match.group(1))
if not listing_id:
print("❗ Could not find listing_id")
exit()We first try extracting from the URL, then fall back to searching the HTML if needed.
Extract Shop ID
The shop ID is embedded in the page's JavaScript data:
# Extract shop ID
shop_id = None
for pattern in [r'"shop_id"\s*:\s*(\d+)', r'"shopId"\s*:\s*(\d+)', r'\'shop_id\'\s*:\s*(\d+)']:
shop_match = re.search(pattern, html)
if shop_match:
shop_id = int(shop_match.group(1))
break
if not shop_id:
print("❗ Could not find shop_id")
exit()We try multiple patterns since Etsy uses different naming conventions in different parts of their code.
Extract CSRF Token
The CSRF token can be in meta tags or inline JavaScript:
# Extract CSRF token
csrf = None
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
for name in ["csrf_nonce", "csrf-token", "x-csrf-token"]:
tag = soup.find("meta", attrs={"name": name})
if tag and tag.get("content"):
csrf = tag["content"]
break
if not csrf:
csrf_match = re.search(r'"csrf_nonce"\s*:\s*"([^"]+)"', html)
if csrf_match:
csrf = csrf_match.group(1)
else:
csrf_match = re.search(r'"csrf_token"\s*:\s*"([^"]+)"', html)
if csrf_match:
csrf = csrf_match.group(1)
if not csrf:
print("⚠️ CSRF token not found, request may fail")
print(f"📋 Listing ID: {listing_id}, Shop ID: {shop_id}")The CSRF token is required for the API request to succeed. Without it, Etsy will reject the request as potentially malicious.
Fetch Reviews with Pagination
Now we make POST requests to the reviews endpoint, paginating through all available reviews. We build the GraphQL payload inside the loop for each page request:
# API endpoint for reviews
deep_url = "https://www.etsy.com/api/v3/ajax/bespoke/member/neu/specs/deep_dive_reviews"
# Scrape reviews with pagination
all_reviews = []
page = 1
while page <= max_pages:
# Build GraphQL payload
payload = {
"log_performance_metrics": True,
"specs": {
"deep_dive_reviews": [
"Etsy\\Modules\\ListingPage\\Reviews\\DeepDive\\AsyncApiSpec",
{
"listing_id": listing_id,
"shop_id": shop_id,
"scope": "listingReviews",
"page": page,
"sort_option": sort_option,
"tag_filters": [],
"should_lazy_load_images": False,
"should_show_variations": False
}
]
},
"runtime_analysis": False
}
# Make POST request through Scrape.do
encoded_deep_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(deep_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_deep_url}&geoCode=us&super=true"
headers = {
"Accept": "application/json, text/plain, */*",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Requested-With": "XMLHttpRequest",
"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"
}
if csrf:
headers["x-csrf-token"] = csrf
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
if response.status_code != 200:
print(f"❗ Request failed with status code {response.status_code}")
breakWe route the POST request through Scrape.do by encoding the review API URL and including the CSRF token in the headers.
Note that for POST requests with JSON payloads, we don't use extraHeaders=true. Instead, Scrape.do automatically forwards the standard headers to Etsy. The sd-x-detected-locale header uses the sd- prefix because it's a custom header specific to our use case.
Parse Review Data from HTML
The API response contains HTML fragments with the review cards. We parse these to extract individual review details:
# Parse response
try:
data = json.loads(response.text)
except:
# Sometimes wrapped in <pre>
soup_resp = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
pre = soup_resp.find("pre")
if pre:
data = json.loads(pre.get_text())
else:
print(f"❗ Failed to parse JSON on page {page}")
break
# Extract reviews from HTML in response
if not data.get("output", {}).get("deep_dive_reviews"):
print(f"📄 Page {page}: No more reviews")
break
review_html = data["output"]["deep_dive_reviews"]
review_soup = BeautifulSoup(review_html, "html.parser")
review_cards = review_soup.find_all("div", class_="review-card")The response JSON contains an output field with an HTML string containing all the review cards for that page.
Extract Rating
Each review card contains a rating input element:
page_reviews = 0
for card in review_cards:
# Extract rating
rating = None
rating_span = card.find("span", class_="wt-display-inline-block")
if rating_span:
rating_input = rating_span.find("input", attrs={"name": "rating"})
if rating_input:
rating = rating_input.get("value")
if rating:
rating = float(rating)The rating value is stored as a string in the input element's value attribute.
Extract Review Text and Metadata
Next, we extract the review text, author name, and creation date:
# Extract review text
review_text_div = card.find("div", class_="wt-text-body")
review_text = review_text_div.get_text(strip=True) if review_text_div else None
# Extract author
author_link = card.find("a", attrs={"data-review-username": True})
author = author_link.get_text(strip=True) if author_link else None
# Extract created date
created_at = None
date_p = card.find("p", class_="wt-text-body-small")
if date_p:
date_text = date_p.get_text(strip=True)
created_at = date_text.split("\n")[-1].strip()
all_reviews.append({
"listing_id": listing_id,
"review_id": card.get("data-review-region"),
"rating": rating,
"text": review_text,
"author": author,
"created_at": created_at
})
page_reviews += 1
print(f"📄 Page {page}: {page_reviews} reviews | Total: {len(all_reviews)}")
if page_reviews == 0:
break
page += 1
time.sleep(0.5)We collect all review data into a dictionary and add it to our list. The script prints progress after each page and adds a small delay to avoid overwhelming the API.
Export Reviews to CSV
Finally, we export all collected reviews to a CSV file. Here's the complete code with the export logic added:
import requests
import urllib.parse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import json
import re
import time
# Configuration
token = "<your-token>"
product_url = "https://www.etsy.com/listing/468670752/a-man-a-dog-the-original-original-wood"
max_pages = 5
sort_option = "Relevancy" # Options: "Relevancy", "MostRecent", "MostHelpful"
# API endpoint for reviews
deep_url = "https://www.etsy.com/api/v3/ajax/bespoke/member/neu/specs/deep_dive_reviews"
# Fetch product page to extract IDs and CSRF token
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(product_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode=us&super=true&extraHeaders=true"
headers = {"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"}
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers)
html = response.text
# Extract listing ID
listing_id = None
listing_match = re.search(r"/listing/(\d+)", product_url)
if listing_match:
listing_id = int(listing_match.group(1))
else:
listing_match = re.search(r'/listing/(\d+)', html)
if listing_match:
listing_id = int(listing_match.group(1))
if not listing_id:
print("❗ Could not find listing_id")
exit()
# Extract shop ID
shop_id = None
for pattern in [r'"shop_id"\s*:\s*(\d+)', r'"shopId"\s*:\s*(\d+)', r'\'shop_id\'\s*:\s*(\d+)']:
shop_match = re.search(pattern, html)
if shop_match:
shop_id = int(shop_match.group(1))
break
if not shop_id:
print("❗ Could not find shop_id")
exit()
# Extract CSRF token
csrf = None
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
for name in ["csrf_nonce", "csrf-token", "x-csrf-token"]:
tag = soup.find("meta", attrs={"name": name})
if tag and tag.get("content"):
csrf = tag["content"]
break
if not csrf:
csrf_match = re.search(r'"csrf_nonce"\s*:\s*"([^"]+)"', html)
if csrf_match:
csrf = csrf_match.group(1)
else:
csrf_match = re.search(r'"csrf_token"\s*:\s*"([^"]+)"', html)
if csrf_match:
csrf = csrf_match.group(1)
if not csrf:
print("⚠️ CSRF token not found, request may fail")
print(f"📋 Listing ID: {listing_id}, Shop ID: {shop_id}")
# Scrape reviews with pagination
all_reviews = []
page = 1
while page <= max_pages:
# Build GraphQL payload
payload = {
"log_performance_metrics": True,
"specs": {
"deep_dive_reviews": [
"Etsy\\Modules\\ListingPage\\Reviews\\DeepDive\\AsyncApiSpec",
{
"listing_id": listing_id,
"shop_id": shop_id,
"scope": "listingReviews",
"page": page,
"sort_option": sort_option,
"tag_filters": [],
"should_lazy_load_images": False,
"should_show_variations": False
}
]
},
"runtime_analysis": False
}
# Make POST request through Scrape.do
encoded_deep_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(deep_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_deep_url}&geoCode=us&super=true"
headers = {
"Accept": "application/json, text/plain, */*",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Requested-With": "XMLHttpRequest",
"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"
}
if csrf:
headers["x-csrf-token"] = csrf
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
if response.status_code != 200:
print(f"❗ Request failed with status code {response.status_code}")
break
# Parse response
try:
data = json.loads(response.text)
except:
# Sometimes wrapped in <pre>
soup_resp = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
pre = soup_resp.find("pre")
if pre:
data = json.loads(pre.get_text())
else:
print(f"❗ Failed to parse JSON on page {page}")
break
# Extract reviews from HTML in response
if not data.get("output", {}).get("deep_dive_reviews"):
print(f"📄 Page {page}: No more reviews")
break
review_html = data["output"]["deep_dive_reviews"]
review_soup = BeautifulSoup(review_html, "html.parser")
review_cards = review_soup.find_all("div", class_="review-card")
page_reviews = 0
for card in review_cards:
# Extract rating
rating = None
rating_span = card.find("span", class_="wt-display-inline-block")
if rating_span:
rating_input = rating_span.find("input", attrs={"name": "rating"})
if rating_input:
rating = rating_input.get("value")
if rating:
rating = float(rating)
# Extract review text
review_text_div = card.find("div", class_="wt-text-body")
review_text = review_text_div.get_text(strip=True) if review_text_div else None
# Extract author
author_link = card.find("a", attrs={"data-review-username": True})
author = author_link.get_text(strip=True) if author_link else None
# Extract created date
created_at = None
date_p = card.find("p", class_="wt-text-body-small")
if date_p:
date_text = date_p.get_text(strip=True)
created_at = date_text.split("\n")[-1].strip()
all_reviews.append({
"listing_id": listing_id,
"review_id": card.get("data-review-region"),
"rating": rating,
"text": review_text,
"author": author,
"created_at": created_at
})
page_reviews += 1
print(f"📄 Page {page}: {page_reviews} reviews | Total: {len(all_reviews)}")
if page_reviews == 0:
break
page += 1
time.sleep(0.5)
# Export to CSV
fields = ["listing_id", "review_id", "rating", "text", "author", "created_at"]
with open("etsy_reviews.csv", "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as f:
writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=fields)
writer.writeheader()
for review in all_reviews:
writer.writerow({k: review.get(k) for k in fields})
print(f"✅ Saved {len(all_reviews)} reviews to etsy_reviews.csv")Running this script will output progress as it scrapes each page:
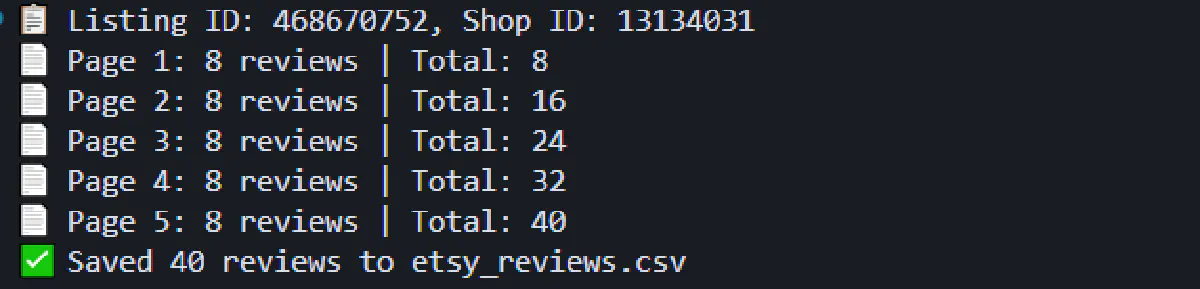
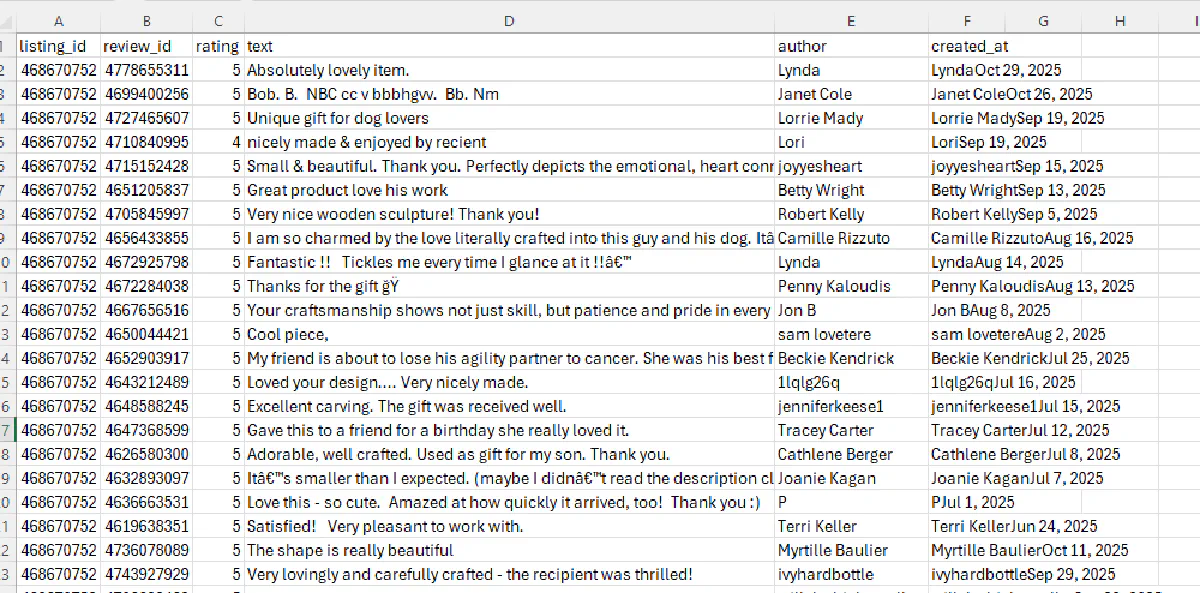
The resulting etsy_reviews.csv file will contain structured review data with all the fields you need for sentiment analysis or quality monitoring:
Extract All Items from Categories
We're going from bottom-to-top, but the last step you need for your complete Etsy scraping workspace is the category scraper, which will extract dozens of items and their prices per request:
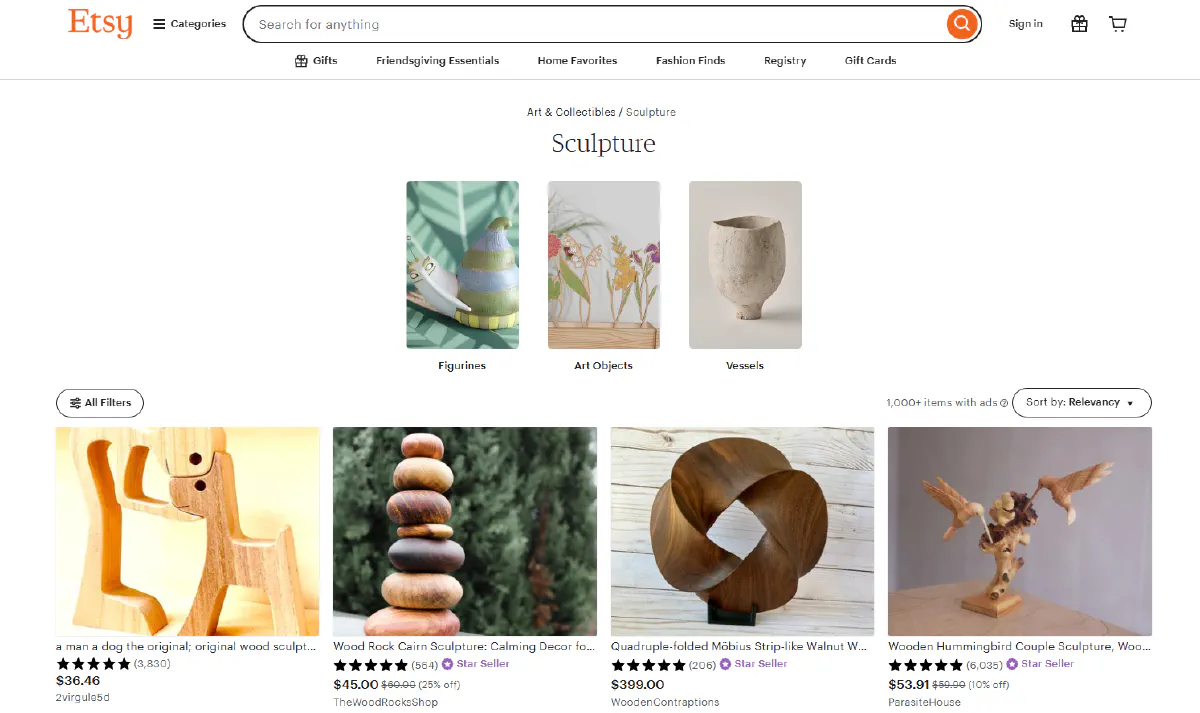
We'll scrape category pages to extract product details, pricing, ratings, and seller information from multiple listings in a single request.
Understanding Categories Page Structure
Etsy category pages like Art & Collectibles > Sculpture display 48 products per page by default.
Each product card contains:
- Product name and URL
- Current price and original price (if discounted)
- Discount percentage
- Product image
- Star rating and review count
- Shop name
- Badges like "Star Seller" or "Free shipping"
- Urgency indicators like "Only 3 left"
The page structure uses standard HTML with CSS classes, making it relatively straightforward to parse with BeautifulSoup once you've bypassed DataDome.
Pagination works through URL query parameters. Adding ?page=2 to the category URL loads the second page of results.
Search results pages follow nearly identical structure to category pages, so the same scraping logic works for both.
Loop Through All Pages of Categories
We'll build a loop that iterates through multiple pages, constructing the paginated URLs and fetching each one:
import requests
import urllib.parse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import re
import time
# Configuration
token = "<your-token>"
base_url = "https://www.etsy.com/c/jewelry"
max_pages = 3
# Scrape all pages
all_products = []
seen = set()
for page_num in range(1, max_pages + 1):
# Build paginated URL
url_parts = urllib.parse.urlsplit(base_url)
params = urllib.parse.parse_qs(url_parts.query)
params["page"] = [str(page_num)]
target_url = urllib.parse.urlunsplit((
url_parts.scheme, url_parts.netloc, url_parts.path,
urllib.parse.urlencode({k: v[0] for k, v in params.items()}),
url_parts.fragment
))
# Make API request
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(target_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode=us&super=true&extraHeaders=true"
headers = {"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"}
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")This code properly handles existing query parameters and adds the page parameter to paginate through results.
Scrape Product Details
Now we extract product information from each card on the page. We start by finding all product links and using them as anchors to locate the full product cards:
page_items = 0
# Extract product cards
for a_tag in soup.select('a[href*="/listing/"]'):
try:
# Get listing ID
url = a_tag.get("href") or ""
if url.startswith("/"):
url = "https://www.etsy.com" + url
listing_match = re.search(r"/listing/(\d+)", url)
listing_id = listing_match.group(1) if listing_match else None
if not listing_id or listing_id in seen:
continue
seen.add(listing_id)We track seen listing IDs to avoid processing duplicates, since some links may appear multiple times on the page.
Extract Name and Image
The product name is typically in the link's title attribute or text content:
# Navigate to card parent
card = a_tag
for _ in range(3):
if card.parent:
card = card.parent
text = card.get_text(" ", strip=True)
# Extract name
name = a_tag.get("title") or a_tag.get_text(" ", strip=True) or "N/A"
# Extract image
image_url = None
img = card.select_one("img")
if img:
image_url = img.get("src") or img.get("data-src") or img.get("data-srcset")
if image_url and " " in image_url and "http" in image_url:
image_url = [p for p in image_url.split() if p.startswith("http")][0]We navigate up the DOM tree to find the full product card, then extract the image from various possible attributes.
Extract Prices and Discount Rate
Price information can include both current and original prices if the item is on sale:
# Extract prices
current_price = original_price = discount_rate = None
currency = None
currency_elem = card.select_one('span.currency-symbol')
if currency_elem:
currency = currency_elem.get_text(strip=True)
price_elem = card.select_one('p.wt-text-title-01.lc-price span.currency-value')
if price_elem:
price_text = price_elem.get_text().replace("$", "").replace(",", "").strip()
current_price = float(price_text) if price_text else None
orig_price_elem = card.select_one('p.wt-text-caption.search-collage-promotion-price span.currency-value')
if orig_price_elem:
orig_text = orig_price_elem.get_text().replace("$", "").replace(",", "").strip()
original_price = float(orig_text) if orig_text else None
if current_price and original_price and original_price > current_price:
discount_rate = round(100 * (original_price - current_price) / original_price, 2)We calculate the discount rate as a percentage if both prices are present.
Extract Rating and Review Count
Rating is stored in aria-label attributes, and review count appears in parentheses:
# Extract rating
rating = None
aria_elem = card.select_one('[aria-label*="out of 5"]')
if aria_elem:
rating_match = re.search(r"([\d.]+)\s*out of 5", aria_elem.get("aria-label", ""))
if rating_match:
rating = float(rating_match.group(1))
# Extract review count
review_count = None
review_match = re.search(r"\((\d{1,5})\)", text)
if review_match:
review_count = int(review_match.group(1))Extract Shop Name and Status Flags
Finally, we extract the shop name and various status indicators:
# Extract shop name
shop = None
shop_elem = card.find('p', {'data-seller-name-container': True})
if shop_elem:
shop_spans = shop_elem.find_all('span')
if len(shop_spans) > 4:
shop = shop_spans[4].get_text(strip=True)
# Extract flags
star_seller = bool(re.search(r"\bStar Seller\b", text, re.I))
free_shipping = bool(re.search(r"\bFree shipping\b", text, re.I))
left_match = re.search(r"Only\s+(\d+)\s+left", text, re.I)
only_left = int(left_match.group(1)) if left_match else None
all_products.append({
"listing_id": listing_id,
"name": name,
"shop": shop,
"price": current_price,
"original_price": original_price,
"discount_rate": discount_rate,
"currency": currency,
"rating": rating,
"review_count": review_count,
"star_seller": star_seller,
"free_shipping": free_shipping,
"only_left": only_left,
"image": image_url,
"url": url
})
page_items += 1
except:
continue
print(f"📄 Page {page_num}: {page_items} items | Total: {len(all_products)}")
if page_num > 1 and page_items == 0:
break
time.sleep(1)We use regex to search for these indicators in the card text, and track urgency with the "Only X left" pattern.
Export to CSV
After scraping all pages, we export the product data to a CSV file with this full code:
import requests
import urllib.parse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import re
import time
# Configuration
token = "<your-token>"
base_url = "https://www.etsy.com/c/jewelry"
max_pages = 3
# Scrape all pages
all_products = []
seen = set()
for page_num in range(1, max_pages + 1):
# Build paginated URL
url_parts = urllib.parse.urlsplit(base_url)
params = urllib.parse.parse_qs(url_parts.query)
params["page"] = [str(page_num)]
target_url = urllib.parse.urlunsplit((
url_parts.scheme, url_parts.netloc, url_parts.path,
urllib.parse.urlencode({k: v[0] for k, v in params.items()}),
url_parts.fragment
))
# Make API request
encoded_url = urllib.parse.quote_plus(target_url)
api_url = f"https://api.scrape.do?token={token}&url={encoded_url}&geoCode=us&super=true&extraHeaders=true"
headers = {"sd-x-detected-locale": "USD|en-US|US"}
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
page_items = 0
# Extract product cards
for a_tag in soup.select('a[href*="/listing/"]'):
try:
# Get listing ID
url = a_tag.get("href") or ""
if url.startswith("/"):
url = "https://www.etsy.com" + url
listing_match = re.search(r"/listing/(\d+)", url)
listing_id = listing_match.group(1) if listing_match else None
if not listing_id or listing_id in seen:
continue
seen.add(listing_id)
# Navigate to card parent
card = a_tag
for _ in range(3):
if card.parent:
card = card.parent
text = card.get_text(" ", strip=True)
# Extract name
name = a_tag.get("title") or a_tag.get_text(" ", strip=True) or "N/A"
# Extract image
image_url = None
img = card.select_one("img")
if img:
image_url = img.get("src") or img.get("data-src") or img.get("data-srcset")
if image_url and " " in image_url and "http" in image_url:
image_url = [p for p in image_url.split() if p.startswith("http")][0]
# Extract prices
current_price = original_price = discount_rate = None
currency = None
currency_elem = card.select_one('span.currency-symbol')
if currency_elem:
currency = currency_elem.get_text(strip=True)
price_elem = card.select_one('p.wt-text-title-01.lc-price span.currency-value')
if price_elem:
price_text = price_elem.get_text().replace("$", "").replace(",", "").strip()
current_price = float(price_text) if price_text else None
orig_price_elem = card.select_one('p.wt-text-caption.search-collage-promotion-price span.currency-value')
if orig_price_elem:
orig_text = orig_price_elem.get_text().replace("$", "").replace(",", "").strip()
original_price = float(orig_text) if orig_text else None
if current_price and original_price and original_price > current_price:
discount_rate = round(100 * (original_price - current_price) / original_price, 2)
# Extract rating
rating = None
aria_elem = card.select_one('[aria-label*="out of 5"]')
if aria_elem:
rating_match = re.search(r"([\d.]+)\s*out of 5", aria_elem.get("aria-label", ""))
if rating_match:
rating = float(rating_match.group(1))
# Extract review count
review_count = None
review_match = re.search(r"\((\d{1,5})\)", text)
if review_match:
review_count = int(review_match.group(1))
# Extract shop name
shop = None
shop_elem = card.find('p', {'data-seller-name-container': True})
if shop_elem:
shop_spans = shop_elem.find_all('span')
if len(shop_spans) > 4:
shop = shop_spans[4].get_text(strip=True)
# Extract flags
star_seller = bool(re.search(r"\bStar Seller\b", text, re.I))
free_shipping = bool(re.search(r"\bFree shipping\b", text, re.I))
left_match = re.search(r"Only\s+(\d+)\s+left", text, re.I)
only_left = int(left_match.group(1)) if left_match else None
all_products.append({
"listing_id": listing_id,
"name": name,
"shop": shop,
"price": current_price,
"original_price": original_price,
"discount_rate": discount_rate,
"currency": currency,
"rating": rating,
"review_count": review_count,
"star_seller": star_seller,
"free_shipping": free_shipping,
"only_left": only_left,
"image": image_url,
"url": url
})
page_items += 1
except:
continue
print(f"📄 Page {page_num}: {page_items} items | Total: {len(all_products)}")
if page_num > 1 and page_items == 0:
break
time.sleep(1)
# Export to CSV
fields = ["listing_id", "name", "shop", "price", "original_price", "discount_rate", "currency",
"rating", "review_count", "star_seller", "free_shipping", "only_left", "image", "url"]
with open("etsy_collection.csv", "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as f:
writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=fields)
writer.writeheader()
for product in all_products:
writer.writerow({k: product.get(k) for k in fields})
print(f"✅ Saved {len(all_products)} products to etsy_collection.csv")The resulting etsy_collection.csv file will contain all the product data structured and ready for analysis:
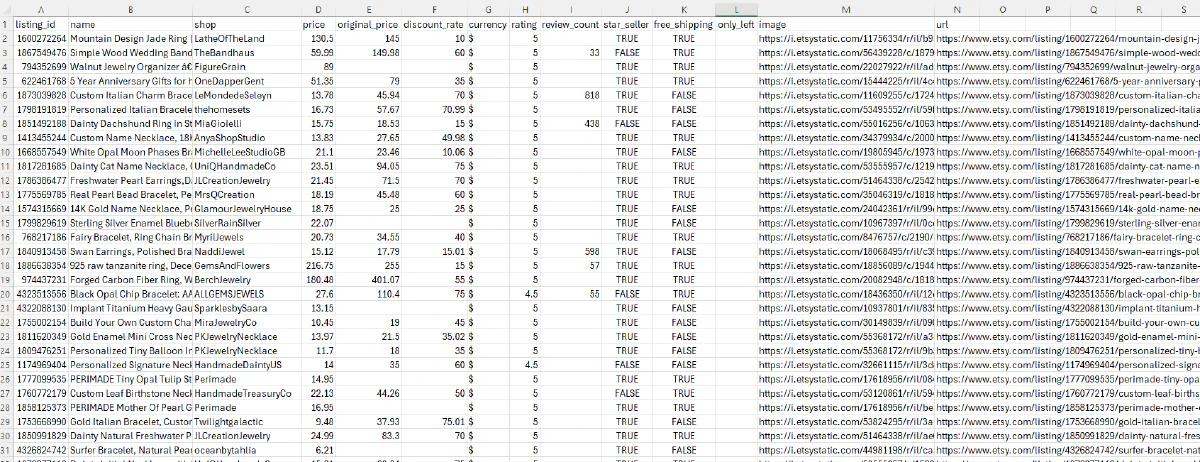
Each row represents a product with fields like listing ID, name, shop, prices, discounts, ratings, review counts, and status flags like Star Seller and Free Shipping.
Conclusion
We covered three core scraping workflows:
- Product pages - Extract structured data from JSON-LD schema for names, prices, ratings, images, and availability
- Reviews - Make authenticated POST requests to Etsy's internal API to fetch paginated review data with ratings, text, and timestamps
- Categories - Parse category and search result pages to build product catalogs with pricing, discounts, seller info, and status indicators
While you scrape thousands of pages from Etsy, Scrape.do handles the hard part:
- Premium residential proxies from real ISPs
- TLS fingerprint spoofing to bypass DataDome
- Automatic session and cookie management
- Geo-targeting for location-specific pricing and shipping

Software Engineer