What is the Difference between Free Proxy and VPN?
You may be a person who cares about your privacy and confidentiality so much that you do not want the sites you visit on the internet to be noticed by the ISP or the sites you visit when you use the internet. In this era where almost all of your information can be stolen and misused by malicious people, it is quite natural to want to protect your privacy while you are on the internet.
There are two different software, Proxy, and VPN, with which you can protect your security and privacy. We have prepared this article for you, in which we explain what these software do, the types of software, the protocol types of the software, and the differences between these software. After reading this article, you will be able to decide what is the right software for you.
As the Scrape.do team, we care deeply about your privacy and security! We strive to maximize your internet experience with the services we offer you. We use all our resources to help you with your slightest problem and solve your problem as soon as possible.
What Do Proxy Servers Do?
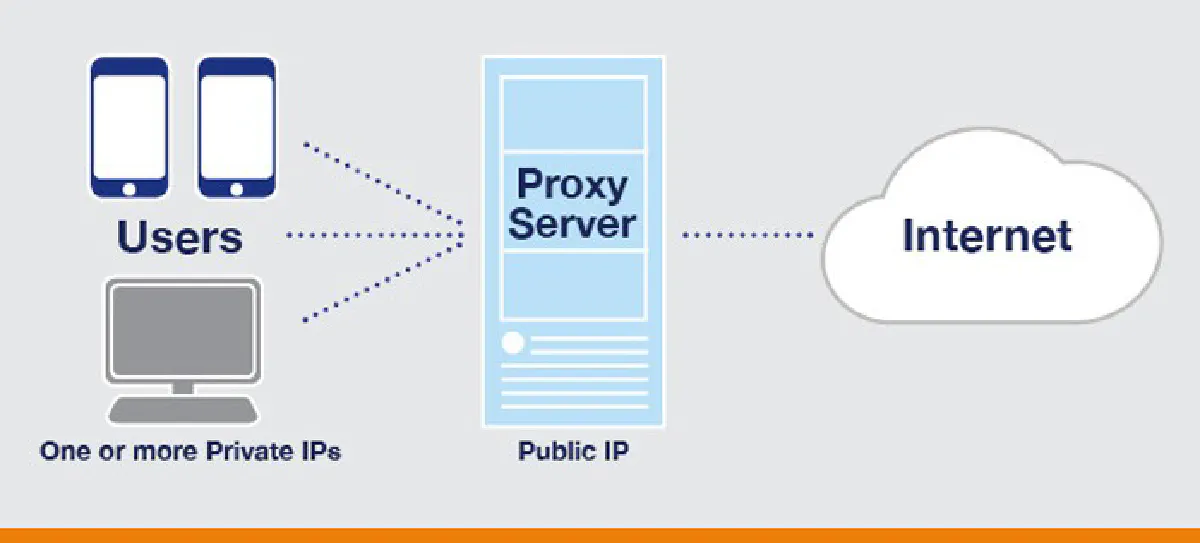
Proxy servers, which are the transition between the websites you visit and the device you use, are programs that should be used by anyone dealing with a business over the internet. Your traffic on the Internet passes through a remote machine designed to connect you to any server. The Web Proxy server hides the original IP address from the internet to see the IP of the proxy belonging to the website, sometimes it has been seen that the computers of other Proxy users are used for this hiding process. Proxies that can only work at the application level will redirect traffic from a single application for which you have installed your proxy and will not encrypt the traffic.
Different Proxy Servers
Proxy servers; There are nine in total, including Reverse Proxy, Web Proxy Server, Anonymous Proxy, High Anonymity Proxy, Transparent Proxy, CGI Proxy, Suffix Proxy, Distorting Proxy, and DNS Proxy. Let’s take a closer look at these Proxy servers!
1. Reverse Proxy
The most important job of the Reverse Proxy server is to listen to the customer’s request and direct the customer to a specific internet server in line with their wishes in case there is more than one website on different servers.
2. Web Proxy Server
Web Proxy servers that forward HTTP requests pass a URL instead of a path and a request is sent to which the Proxy server will respond. The problems of multiple Proxy servers are solved in such servers where the client-server Proxy auto-configuration protocol is used.
3. Anonymous Proxy
Anonymous Proxy servers, a server is known for not creating an original and valid IP address, are detectable, but these servers also have the task of providing rational anonymity to the device that is the information client.
4. High Anonymity Proxy
High Anonymity Proxy provides a more anonymous service than Anonymous Proxy. This Proxy, which does not allow the original IP address to be detected under any circumstances, cannot be detected by anyone.
5. Transparent Proxy
Transparent Proxy, which never provides anonymity to the client and can be easily identified as an original IP address, is also used to act as a cache for websites.
6. CGI Proxy
Developed to make websites more accessible, CGI Proxy is responsible for accepting and processing targeting requests of URL addresses using an internet form and returning the result to the web browser.
7. Suffix Proxy
Suffix Proxy, which adds the proxy name to the URL to the content requested from the proxy and does not have a high level of anonymity, is used by many people to bypass the filters on the websites. Although it is easy to implement this Proxy, which is very easy to use, it has a lower usage rate due to increased internet filters.
8. Distorting Proxy
Distorting Proxy is a proxy that uses HTTP headers to protect its privacy, replacing the original IP addresses with a completely false IP address to protect the privacy of the clients after the proxy servers are detected.
9. DNS Proxy
DNS Proxy, which is completely different from other Proxy types and receives all requests in the form of DNS queries, is responsible for forwarding the requests it receives to the Domain server, where they can be cached, and routing the request flow from there.
Types of Proxy Server Protocols
We have briefly explained the four Proxy Server Protocols for you, namely Socks Proxy Server, FTP Proxy Server, HTTP Proxy Server, and SSL Proxy Server!
Socks Proxy Server: Socks Proxy Server, which is responsible for providing a connection to a specific server, helps different data types such as TCS or UDP to become more layered depending on their protocols.
FTP Proxy Server: The FTP Proxy Server, which caches all the traffic of FTP requests, is a server responsible for transferring these requests.
HTTP Proxy Server: HTTP Proxy, which uses HTTP protocols, is frequently used by experts to process a one-way request to internet pages.
SSL Proxy Server: SSL Proxy Server, which uses SOCKS Proxy protocol to allow appropriate requests of internet pages, is a Proxy server developed using TCP relay.
What is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
A VPN is basically like a proxy, redirecting your internet traffic through a remote server and hiding your IP address so websites cannot see your real IP address or location. However, while Proxy servers work at the application level, VPN addresses work at the operating system level and completely replace and redirect traffic from your browser or background application. The VPN also encrypts the traffic between the Internet connection and the client device, preventing your Internet Service Provider from seeing what you are doing online. VPN encryption will additionally protect you from government surveillance, hackers, and website tracking.
Types of Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
The most commonly used VPN types are Remote Access VPN, Site-to-Site VPN, Intranet Based VPN, and Extranet Based VPN.
Remote Access VPN: Allowing an internet user to connect to a remote private network and access all the services and resources of this internet remotely, Remote Access VPN takes place over the Internet, which is a secure and private connection. This type of VPN is useful for both home internet users and workplace internet users.
Site-to-Site VPN: Site-to-Site VPN, also called Router-to-Router VPN and used quite frequently in large companies, is used among companies and organizations with branches in different locations.
Intranet-based VPN: The VPN used when the same company has more than one office and they are connected using Site-to-Site VPN is called Intranet-based VPN.
Extranet-based VPN: When a company uses a Site-to-Site VPN to connect to another company’s office, it is called Extranet-based VPN.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Protocol Types
We can list the protocols used specifically for VPNs as Internet Protocol Security (IPSec), Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), OpenVPN, Secure Shell (SSH), SSL, and TLS. Read on to learn about these protocols with different features!
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec): Used to secure Internet communication on an IP network, Internet Protocol Security carefully encrypts each data packet during Internet connection, protecting Internet protocol interaction by authenticating the Internet session. IPSec VPN works in two different modes, Transport Mode and Tunneling Mode. The tunnel mode is responsible for encrypting the entire data packet, while the transport mode’s task is to encrypt the messages in the data packet so that only the reader can understand it.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP): A tunneling protocol that combines with another security protocol, such as IPSec, to establish a secure VPN connection, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol tunnels between two L2TP ports.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP): Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, which creates a tunnel and encrypts and confines the data packet, is one of the most commonly used VPN protocols and has been used since the first version of Windows. This protocol can be used in Mac and Linux operating systems besides Windows.
SSL and TLS: SSL, which stands for Secure Sockets Layer, and TSL, which is Transport Layer Security, create a VPN that an internet browser will treat as a client and where user access to certain applications is prohibited. TLS and SSL protocol, which are frequently used in online shopping sites, is also integrated with internet browsers. Internet browsers do not require any action to switch to the SSL protocol. The URL addresses where SSL connections are used are preceded by HTTPS, not HTTP.
OpenVPN: An open-source VPN that is frequently used to create Point-to-Point or Site-to-Site connections, OpenVPN uses a security protocol based on the SSL and TLS protocol.
Secure Shell (SSH): Secure Shell, which creates VPN tunnels where data transfer takes place and ensures that these tunnels are encrypted separately, has its own connections and client. Data using this protocol is sent from a local port to a remote server with an encrypted tunnel created by SSH VPN.
What are the Differences Between Proxy and VPN?
Although VPNs and Proxy Servers seem similar in terms of their intended use and features during use, this two software have many different features. If you are confused about whether you need a VPN or a Proxy Server, read this comparison we prepared for you and your confusion will be cleared up a lot!
Which One Is More Reliable?
Proxy servers, which can easily hide your identity from websites, cannot show the same performance in hiding your connection. Using a proxy server that cannot encrypt your connection will offer a less secure connection than connecting to a web server with a browser. VPNs, which are a more reliable solution than proxies, are tasked with encrypting data just before sending it to the client. So VPNs will hide your identity from the internet and ISP.
Which One Gives More Importance to Privacy?
While VPN and Proxy Servers are tasked with effectively hiding the IP address of the people using them, they will process the data presented to them in quite different ways. Although proxy servers, which see themselves as an intermediary between an internet user and the internet, will hide the IP address of the internet user from the internet server visited by the users, they cannot fully provide the security received from this website and given to the website. This will result quite differently when you use a VPN.
VPNs that hide the IP address and location of the internet user, thus preventing them from being identified, provide true privacy for the internet user by using end-to-end encryption so that an ISP or router cannot access the internet user’s data. In addition, even if the data encrypted by the VPN is captured by malicious internet users, they will not be able to access the data unless they can decrypt it.
Which One Is Faster?
Proxy, which is a server that can be used by many internet users at the same time, can cause connection speed delays when used. If you are planning to use a free proxy connection, we can say that your internet connection will be quite slow. Although the use of a VPN server far from the internet user’s location will also cause the connection speed to decrease, a VPN provider with the right technology will not make you feel that there is a delay.
If you have any questions after this article where we talked about the detailed information about proxy and VPN and the difference between this two software, do not hesitate to ask us! We strive to give you the best service.